Don’t Feel Like a Chump When You Close on Your New Mortgage

Mortgage closing costs dropped 7 percent over the past year, falling to $1,847 on a $200,000 loan, according to a new analysis by Bankrate.
Typical closing costs varied by state, ranging from $2,163 in Hawaii to $1,613 in Ohio. You can find the average rate for your state in the table below.
Lenders compete for business, so shopping around with at least three mortgage providers can help you reduce the fees associated with your loan. “Homebuyers have more say over closing costs than they think,” Bankrate Senior Mortgage Analyst Holden Lewis said in a statement.
Even as banks lower their mortgage fees, they’re increasing fees in most other categories, according to MoneyRates.com.
While lower mortgage fees are good news for homebuyers and those refinancing their loans, the average saving amount to just $140. That’s not much relative to the total costs associated with buying a house. The average down payment for homebuyers in the first quarter of 2015 was $57,710, for example.
Related: Want Your Own Home? Here’s How to Do the Math
The costs don’t stop once the buyers move in. On top of mortgage payments, homeowners face an average of more than $6,000 in additional costs related to their house, including homeowners insurance, property taxes and utilities.
The National Association of Realtors expects home prices to increase 6.5 percent this year to a median $221,900, which would put them at the same level as their 2006 record high.
For buyers, better news than the lower mortgage fees is that rates remain relatively low, falling to 3.98 percent last week, per Freddie Mac.
Closing costs | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| State | Average origination fees | Average third-party fees | Average origination plus third-party fees |
| Alabama | $1,066 | $776 | $1,842 |
| Alaska | $935 | $922 | $1,857 |
| Arizona | $1,208 | $761 | $1,969 |
| Arkansas | $1,057 | $760 | $1,817 |
| California | $937 | $896 | $1,834 |
| Colorado | $1,192 | $719 | $1,910 |
| Connecticut | $1,074 | $960 | $2,033 |
| Delaware | $904 | $924 | $1,828 |
| District of Columbia | $1,077 | $718 | $1,794 |
| Florida | $1,028 | $778 | $1,806 |
| Georgia | $1,058 | $821 | $1,879 |
| Hawaii | $1,033 | $1,130 | $2,163 |
| Idaho | $894 | $788 | $1,682 |
| Illinois | $1,080 | $767 | $1,847 |
| Indiana | $1,067 | $770 | $1,837 |
| Iowa | $1,161 | $762 | $1,923 |
| Kansas | $1,047 | $753 | $1,800 |
| Kentucky | $1,060 | $737 | $1,797 |
| Louisiana | $1,060 | $817 | $1,877 |
| Maine | $897 | $830 | $1,727 |
| Maryland | $1,093 | $742 | $1,835 |
| Massachusetts | $905 | $851 | $1,756 |
| Michigan | $1,072 | $746 | $1,818 |
| Minnesota | $1,067 | $689 | $1,757 |
| Mississippi | $1,046 | $837 | $1,884 |
| Missouri | $1,040 | $792 | $1,833 |
| Montana | $1,062 | $855 | $1,917 |
| Nebraska | $1,047 | $770 | $1,817 |
| Nevada | $1,002 | $848 | $1,850 |
| New Hampshire | $1,084 | $750 | $1,835 |
| New Jersey | $1,181 | $913 | $2,094 |
| New Mexico | $1,076 | $876 | $1,952 |
| New York | $1,032 | $879 | $1,911 |
| North Carolina | $1,036 | $875 | $1,911 |
| North Dakota | $1,045 | $791 | $1,836 |
| Ohio | $933 | $681 | $1,613 |
| Oklahoma | $1,027 | $734 | $1,761 |
| Oregon | $1,080 | $785 | $1,864 |
| Pennsylvania | $1,055 | $678 | $1,733 |
| Rhode Island | $1,093 | $802 | $1,896 |
| South Carolina | $1,058 | $837 | $1,895 |
| South Dakota | $1,055 | $704 | $1,759 |
| Tennessee | $1,033 | $773 | $1,806 |
| Texas | $1,031 | $833 | $1,864 |
| Utah | $909 | $788 | $1,697 |
| Vermont | $1,074 | $862 | $1,936 |
| Virginia | $1,050 | $787 | $1,837 |
| Washington | $1,077 | $824 | $1,901 |
| West Virginia | $1,067 | $904 | $1,971 |
| Wisconsin | $1,047 | $723 | $1,770 |
| Wyoming | $874 | $814 | $1,689 |
| Average | $1,041 | $807 | $1,847 |
Bankrate.com surveyed up to 10 lenders in each state in June 2015 and obtained online Good Faith Estimates for a $200,000 mortgage to buy a single-family home with a 20 percent down payment in a prominent city. Costs include fees charged by lenders, as well as third-party fees for services such as appraisals and credit reports. The survey excludes title insurance, title search, taxes, property insurance, association fees, interest and other prepaid items.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- You’re Richer Than You Think. Really.
- The 10 Fastest-Growing Jobs Right Now
- The 5 Worst Cities to Raise a Family
Deficit Hits $738.6 Billion in First 8 Months of Fiscal Year

The U.S. budget deficit grew to $738.6 billion in the first eight months of the current fiscal year – an increase of $206 billion, or 38.8%, over the deficit recorded during the same period a year earlier. Bloomberg’s Sarah McGregor notes that the big increase occurred despite a jump in tariff revenues, which have nearly doubled to $44.9 billion so far this fiscal year. But that increase, which contributed to an overall increase in revenues of 2.3%, was not enough to make up for the reduced revenues from the Republican tax cuts and a 9.3% increase in government spending.
Tweet of the Day: Revenues or Spending?

Rep. Kevin Brady (R-TX), ranking member of the House Ways and Means Committee and one of the authors of the 2017 Republican tax overhaul, told The Washington Post’s Heather Long Tuesday that the budget deficit is driven by excess spending, not a shortfall in revenues in the wake of the tax cuts. The Wall Street Journal’s Kate Davidson provided some inconvenient facts for Brady’s claim in a tweet, pointing out that government revenues as a share of GDP have fallen significantly since 2015, while spending has remained more or less constant.
Chart of the Day: The Decline in IRS Audits

Reviewing the recent annual report on tax statistics from the IRS, Robert Weinberger of the Tax Policy Center says it “tells a story of shrinking staff, fewer audits, and less customer service.” The agency had 22% fewer personnel in 2018 than it did in 2010, and its enforcement budget has fallen by nearly $1 billion, Weinberger writes. One obvious effect of the budget cuts has been a sharp reduction in the number of audits the agency has performed annually, which you can see in the chart below.
Number of the Day: $102 Million

President Trump’s golf playing has cost taxpayers $102 million in extra travel and security expenses, according to an analysis by the left-leaning HuffPost news site.
“The $102 million total to date spent on Trump’s presidential golfing represents 255 times the annual presidential salary he volunteered not to take. It is more than three times the cost of special counsel Robert Mueller’s investigation that Trump continually complains about. It would fund for six years the Special Olympics program that Trump’s proposed budget had originally cut to save money,” HuffPost’s S.V. Date writes.
Date says the White House did not respond to HuffPost’s requests for comment.
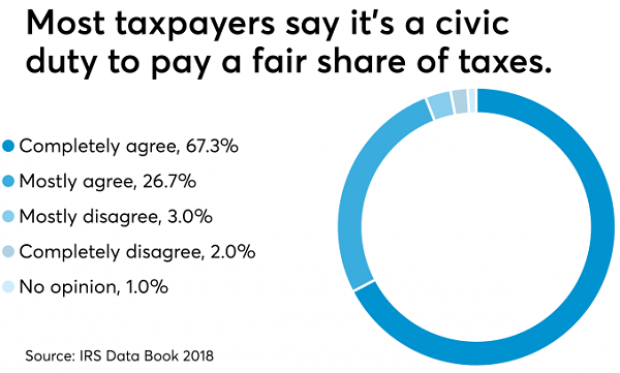
Americans See Tax-Paying as a Duty

The IRS may not be conducting audits like it used to, but according to the agency’s Data Book for 2018, most Americans still believe it’s not acceptable to cheat on your taxes. About 67% of respondents to an IRS opinion survey “completely agree” that it’s a civic duty to pay “a fair share of taxes,” and another 26% “mostly agree,” bringing the total in agreement to over 90%. Accounting Today says that attitude has been pretty consistent over the last decade.