The Washington Post Closes a Window on Hackers and Big Government

The Washington Post is pushing back against government surveillance, hackers and other nosy folks trying to get a peek at you and your data.
Starting Tuesday it will begin to encrypt parts of its website to make it more difficult to track the reading habits of visitors. The encryption will apply to the Post’s homepage, stories on the site’s national security page and The Switch, its technology policy blog.
A display icon of a small lock in the web address bar will signal readers that pages are encrypted. In addition, the secure pages will start with the letters “https,” rather than the standard “http.”
The encryption also has the potential to make it tougher for governments to censor content. If censors are monitoring website traffic, they can see only the domain a person is visiting, not the specific page. A country would have to block the entire website if it wanted to block content.
The Post acknowledges that the additional security measures could make online advertising less attractive to companies. Advertisers might also be driven away by having to make sure their content is also secure, an extra step some companies might not be willing to take.
The Post is the first major news organization to introduce such security measures. Last fall, The New York Times published a blog post imploring websites to implement secure connections, but it has yet to follow through on its own challenge.
However, other smaller news sources, such as the Intercept and TechDirt, use https technology by default.
Encrypted traffic is becoming increasingly common for many sites, including online banking and web-based email services. Earlier this month, the Obama administration ordered all public federal websites to begin using https technology by the end of 2016.
The social media giant Facebook announced in early June that users could encrypt notifications sent from the website to a user’s personal email address, protecting potentially sensitive emails. Facebook – as well as hackers, spies and others -- will be denied access to the user’s private encryption key.
This move prevents hackers who have accessed a user’s email inbox from being able to understand emails from Facebook without knowing their private key. While a user’s activity on the actual site will not be encrypted, this announcement could be the first in a series of moves to protect Facebooks’ user privacy.
Apple and Google have also implemented more security measures for user privacy over the last year.
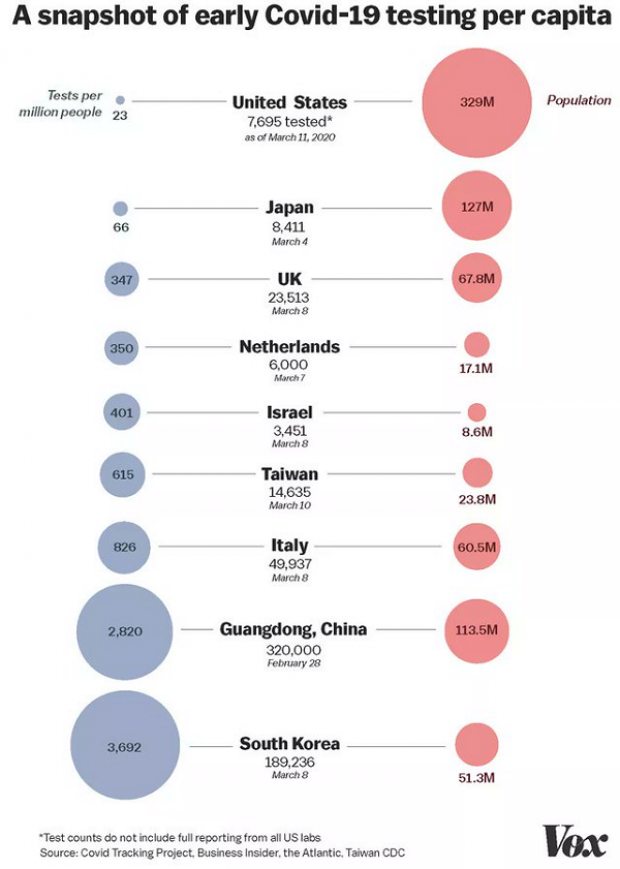
Chart of the Day: Long Way to Go on Coronavirus Testing

The White House on Friday unveiled plans for a new effort to ramp up testing for Covid-19, which experts say is an essential part of limiting the spread of the virus. This chart from Vox gives a sense of just how far the U.S. has to go to catch up to other countries that are dealing with the pandemic, including South Korea, the leading virus screener with 3,692 tests per million people. The U.S., by comparison, has done about 23 tests per million people as of March 12.
After Spending $2 Billion, Air Force Bails Out on Planned Upgrades of B-2 Bombers

The Air Force has scrapped a planned upgrade of its B-2 stealth bomber fleet — even after spending $2 billion on the effort — because defense contractor Northrup Grumman didn’t have the necessary software expertise to complete the project on time and on budget, Bloomberg’s Anthony Capaccio reports, citing the Pentagon’s chief weapons buyer.
Ellen Lord, the undersecretary of defense for acquisition and sustainment, told reporters that the nearly $2 billion that had already been spent on the program wasn’t wasted because “we are still going to get upgraded electronic displays.”
Big Hurdle for Sanders’ Plan to Cancel Student Debt

Bernie Sanders wants to eliminate $1.6 trillion in student debt, to be paid for by a tax on financial transactions, but doing so won’t be easy, says Josh Mitchell of The Wall Street Journal.
The main problem for Sanders is that most Americans don’t support the plan, with 57% of respondents in a poll last fall saying they oppose the idea of canceling all student debt. And the politics are particularly thorny for Sanders as he prepares for a likely general election run, Mitchell says: “Among the strongest opponents are groups Democrats hope to peel away from President Trump: Rust Belt voters, independents, whites, men and voters in rural areas.”
Number of the Day: $7 Million

That’s how much Michael Bloomberg is spending per day in his pursuit of the Democratic presidential nomination, according to new monthly filings with the Federal Election Commission. “In January alone, Bloomberg dropped more than $220 million on his free-spending presidential campaign,” The Hill says. “That breaks down to about $7.1 million a day, $300,000 an hour or $5,000 per minute.”