Science Confirms: Watching Online Cat Videos Is Good for You

Looking at Grumpy Cat’s underbite and feline dwarfism just might just make you feel better about your bratty kid, your nagging spouse or your demanding boss. That’s right, according to a new study published in the journal Computers in Human Behavior, watching cat videos online reduces our negative feelings while raising our sense of well-being and boosting our energy levels.
Grumpy Cat, whose real pet name is Tardar Sauce, shares a manager with fellow YouTube stars Keyboard Cat and Nyan Cat. Last we checked, the famous feline had 7.7 million Likes on Facebook. In all, more than 2 million cat videos were posted on YouTube last year, gathering nearly 26 billion views. Cat videos had more views per video than any other category of YouTube content. That makes kittens more valuable eye candy than, say, Maxim’s Hot 100. (Taylor Swift topped the list this year, just in case you were wondering.)
Related: The Internet Power of Kim Kardashian’s Butt
For the new study, Jessica Gall Myrick, an assistant professor at the Indiana University Media School, surveyed nearly 7,000 Internet users about how watching cat videos affects their moods. She got a little help from Bloomington, Indiana resident Mike Bridavsky — the owner of Internet celebrity cat Lil Bub — who used social media to recruit participants for the survey.
The results should make you feel a bit less guilty about clicking through one cat video after another: “Even if they are watching cat videos on YouTube to procrastinate or while they should be working, the emotional pay-off may actually help people take on tough tasks afterward,” Myrick says.
Don’t think watching cat videos online is a pop culture phenomenon worthy of academic research? Myrick disagrees: “If we want to better understand the effects the Internet may have on us as individuals and on society, then researchers can’t ignore Internet cat videos anymore.”
Read the original paper on emotion regulation procrastination, and watching cat videos online here.
Tax Refunds Rebound

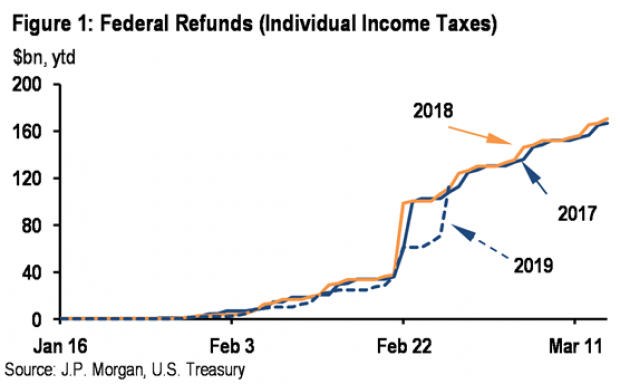
Smaller refunds in the first few weeks of the current tax season were shaping up to be a political problem for Republicans, but new data from the IRS shows that the value of refund checks has snapped back and is now running 1.3 percent higher than last year. The average refund through February 23 last year was $3,103, while the average refund through February 22 of 2019 was $3,143 – a difference of $40. The chart below from J.P. Morgan shows how refunds performed over the last 3 years.
Number of the Day: $22 Trillion

The total national debt surpassed $22 trillion on Monday. Total public debt outstanding reached $22,012,840,891,685.32, to be exact. That figure is up by more than $1.3 trillion over the past 12 months and by more than $2 trillion since President Trump took office.
Chart of the Week: The Soaring Cost of Insulin
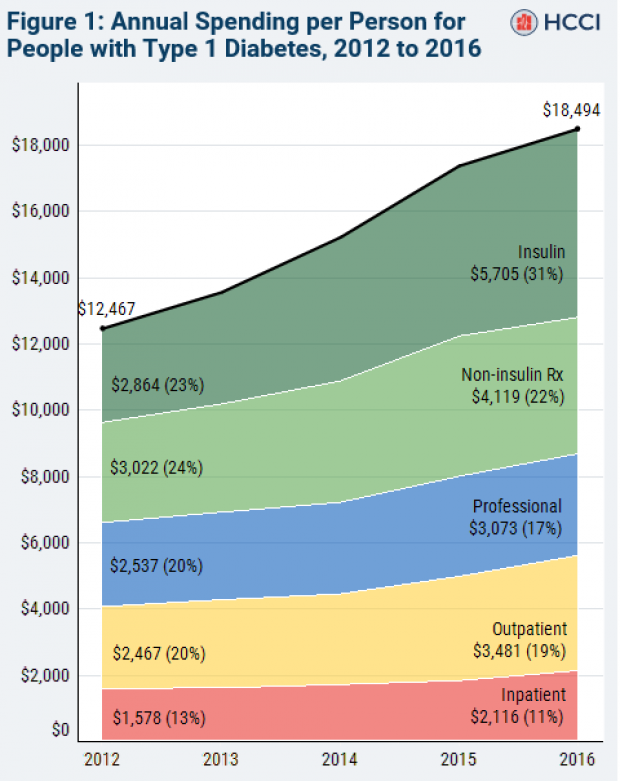
The cost of insulin used to treat Type 1 diabetes nearly doubled between 2012 and 2016, according to an analysis released this week by the Health Care Cost Institute. Researchers found that the average point-of-sale price increased “from $7.80 a day in 2012 to $15 a day in 2016 for someone using an average amount of insulin (60 units per day).” Annual spending per person on insulin rose from $2,864 to $5,705 over the five-year period. And by 2016, insulin costs accounted for nearly a third of all heath care spending for those with Type 1 diabetes (see the chart below), which rose from $12,467 in 2012 to $18,494.
Chart of the Day: Shutdown Hits Like a Hurricane

The partial government shutdown has hit the economy like a hurricane – and not just metaphorically. Analysts at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget said Tuesday that the shutdown has now cost the economy about $26 billion, close to the average cost of $27 billion per hurricane calculated by the Congressional Budget Office for storms striking the U.S. between 2000 and 2015. From an economic point of view, it’s basically “a self-imposed natural disaster,” CRFB said.
Chart of the Week: Lowering Medicare Drug Prices
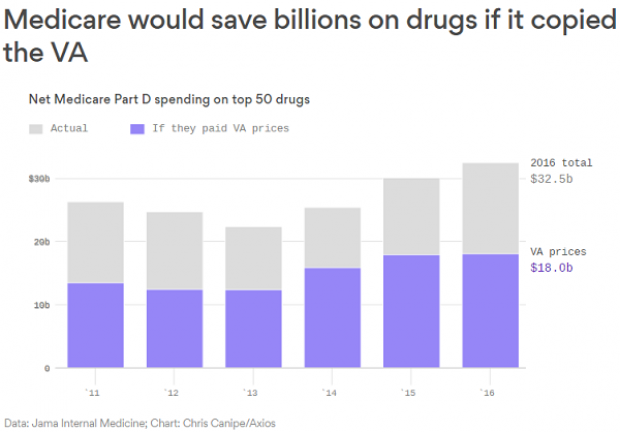
The U.S. could save billions of dollars a year if Medicare were empowered to negotiate drug prices directly with pharmaceutical companies, according to a paper published by JAMA Internal Medicine earlier this week. Researchers compared the prices of the top 50 oral drugs in Medicare Part D to the prices for the same drugs at the Department of Veterans Affairs, which negotiates its own prices and uses a national formulary. They found that Medicare’s total spending was much higher than it would have been with VA pricing.
In 2016, for example, Medicare Part D spent $32.5 billion on the top 50 drugs but would have spent $18 billion if VA prices were in effect – or roughly 45 percent less. And the savings would likely be larger still, Axios’s Bob Herman said, since the study did not consider high-cost injectable drugs such as insulin.