The Woefully Distorted Federal Policies on Child Abuse
Here’s something just in from the world of grossly distorted government policy:
Every year, roughly 680,000 children are reported victims of neglect or abuse by their parents in this country – a tragic statistic reflective of troubling societal, psychological and economic problems. Even worse, 1,520 children died from maltreatment in 2013, nearly 80 percent of them at the hands of their own parents.
Related: Feds Blow $100 Billion Annually on Incorrect Payments
Federal and state authorities over the years have developed a large and costly system for reporting and investigating maltreatment, removing endangered children from their homes, and preventing and treating problems of parents and children.
But as a new study touted on Wednesday by the Brookings Institution concludes, the federal government provides states with far more money to support kids once they have been removed from their homes and placed in foster care than it provides for prevention and treatment programs to keep the kids out of foster homes in the first place.
And the disparity is startling.
Two of the largest grant programs in Title IV-B of the Social Security Act provide states with funding totaling around $650 million annually for “front end” services designed to prevent or treat parent and child problems that contribute to abuse and neglect. They address problems such as substance abuse, family violence and mental health issues.
Related: Time to Stop Social Safety Net Child Abuse
Yet another series of programs in Title IV-E of the Social Security law provides states with open-ended funding that totaled about $6.9 billion in 2014. Those funds pay almost exclusively for out-of-home care for children from poor families, along with the administrative and training expenses associated with foster care, adoption, and guardianship.
That’s a 10 to 1 disparity in funding for the two efforts – one to try to hold families together and the other to move children out of their homes and into foster care.
“Congress has the opportunity to change the funding formula under Title IV of the Social Security Act so that states have the flexibility to put money where it will be most effective at keeping at-risk children safe, ensuring that they have a permanent home, and promoting their well-being,” wrote Ron Haskins, Lawrence M. Berger and Janet Currie, the authors of the study.
In their policy brief, “Can States Improve Children’s Health by Preventing Abuse and Neglect,” Haskins, a Senior Fellow in Economic Studies at Brookings, Currie of Princeton University and Berger of the University of Wisconsin-Madison, write that revising the grant programs could improve the welfare of children who are at risk of abuse or neglect.
This is something else that lawmakers might consider later this year when they begin to focus on disability insurance and other programs within the Social Security law.
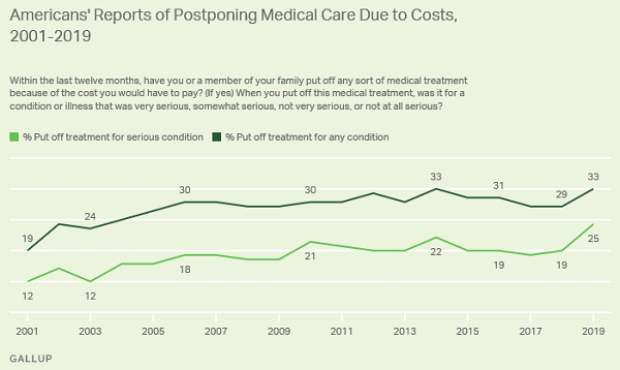
Increasing Number of Americans Delay Medical Care Due to Cost: Gallup

From Gallup: “A record 25% of Americans say they or a family member put off treatment for a serious medical condition in the past year because of the cost, up from 19% a year ago and the highest in Gallup's trend. Another 8% said they or a family member put off treatment for a less serious condition, bringing the total percentage of households delaying care due to costs to 33%, tying the high from 2014.”
Number of the Day: $213 Million

That’s how much the private debt collection program at the IRS collected in the 2019 fiscal year. In the black for the second year in a row, the program cleared nearly $148 million after commissions and administrative costs.
The controversial program, which empowers private firms to go after delinquent taxpayers, began in 2004 and ran for five years before the IRS ended it following a review. It was restarted in 2015 and ran at a loss for the next two years.
Senate Finance Chairman Chuck Grassley (R-IA), who played a central role in establishing the program, said Monday that the net proceeds are currently being used to hire 200 special compliance personnel at the IRS.
US Deficit Up 12% to $342 Billion for First Two Months of Fiscal 2020: CBO

The federal budget deficit for October and November was $342 billion, up $36 billion or 12% from the same period last year, the Congressional Budget Office estimated on Monday. Revenues were up 3% while outlays rose by 6%, CBO said.
Hospitals Sue to Protect Secret Prices

As expected, groups representing hospitals sued the Trump administration Wednesday to stop a new regulation would require them to make public the prices for services they negotiate with insurers. Claiming the rule “is unlawful, several times over,” the industry groups, which include the American Hospital Association, say the rule violates their First Amendment rights, among other issues.
"The burden of compliance with the rule is enormous, and way out of line with any projected benefits associated with the rule," the suit says. In response, a spokesperson for the Department of Health and Human Services said that hospitals “should be ashamed that they aren’t willing to provide American patients the cost of a service before they purchase it.”
See the lawsuit here, or read more at The New York Times.
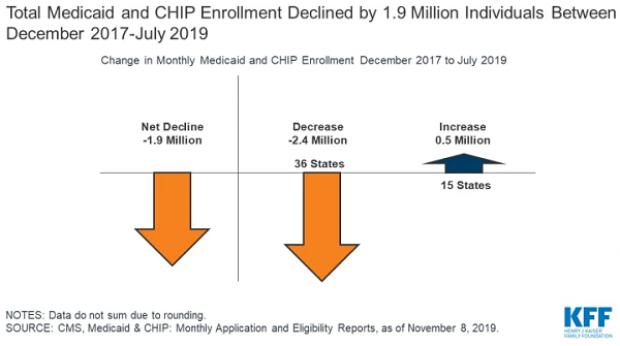
A Decline in Medicaid and CHIP Enrollment
Between December 2017 and July 2019, enrollment in Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) fell by 1.9 million, or 2.6%. The Kaiser Family Foundation provided an analysis of that drop Monday, saying that while some of it was likely caused by enrollees finding jobs that offer private insurance, a significant portion is related to enrollees losing health insurance of any kind. “Experiences in some states suggest that some eligible people may be losing coverage due to barriers maintaining coverage associated with renewal processes and periodic eligibility checks,” Kaiser said.