Republicans Push Ahead on Medicaid Restrictions

The Trump administration on Friday approved Ohio’s request to impose work requirements on Medicaid recipients. Starting in 2021, the state will require most able-bodied adults aged 19 to 49 to either work, go to school, be in job training or volunteer for 80 hours a month in order to receive Medicaid benefits. Those who fail to meet the requirements over 60 days will be removed from the system, although they can reapply immediately.
The new work requirements include exemptions for pregnant women, caretakers and those living in counties with high unemployment rates and will apply only to those covered through the expansion of Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act. There are currently about 540,000 people on Medicaid in Ohio who receive coverage through the expansion, according to Kaitlin Schroeder of The Dayton Daily News, compared to roughly 2.6 million Medicaid recipients in the state overall.
Once implemented, the work requirements are expected to result in 36,000 people losing their Medicaid eligibility, according to state officials, though critics say the reductions could be significantly larger. Similar work requirements in Arkansas pushed 18,000 people off the Medicaid rolls in six months.
A larger GOP project: The creation of new work requirements is part of a larger effort by Republicans to limit the expansion of Medicaid, says The Wall Street Journal’s Stephanie Armour. Since the Affordable Care Act passed in 2010, 36 states have expanded their Medicaid programs under the ACA and the number of people in the program has grown by 50 percent, from roughly 50 million to about 75 million. But many red-state governors have expressed concerns about the cost of Medicaid expansion and worries about a lack of self-sufficiency among the able-bodied poor, and are embracing new limitations on the program for both fiscal and political reasons.
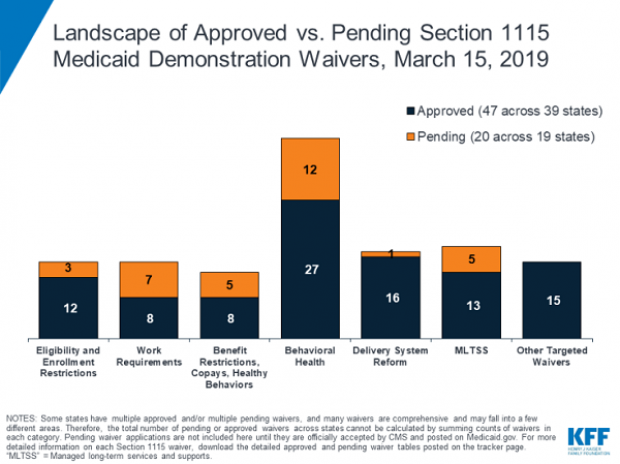
In 2017, the White House in 2017 gave states the green light to explore ways to limit the reach and expense of their Medicaid programs. Governors have proposed a variety of new rules, which require waivers from the federal government to enact. Kentucky, for example, wants to drug-test Medicaid recipients, and Utah wants a partial expansion and a cap on payments. Kaiser Health News summarizes the variety of waivers states have requested, which are governed by Section 1115 of the Social Security Act, in the chart below.
Legal challenges: Efforts to restrict Medicaid have received legal challenges, and U.S. District Judge James Boasberg blocked work requirements in Kentucky last year. The same judge, who has expressed doubts about the administration’s approach to Medicaid, will rule on the legality of work requirements in both Kentucky and Arkansas by April 1.
The bottom line: The Trump administration is seeking fundamental changes in how Medicaid works. Even if Boasberg rules against work requirements, expect the White House and Republican governors to continue to push for new limitations on the program.
Map of the Day: Navigating the IRS

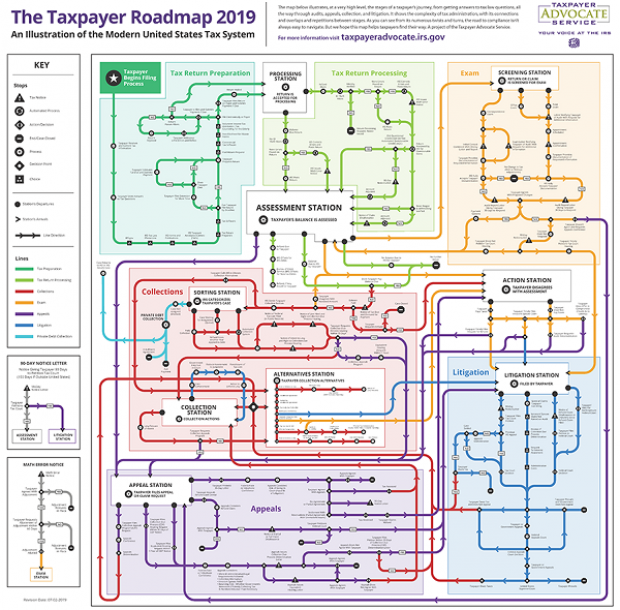
The Taxpayer Advocate Service – an independent organization within the IRS whose roughly 1,800 employees both assist taxpayers in resolving problems with the tax collection agency and recommend changes aimed at improving the system – released a “subway map” that shows the “the stages of a taxpayer’s journey.” The colorful diagram includes the steps a typical taxpayer takes to prepare and file their tax forms, as well as the many “stations” a tax return can pass through, including processing, audits, appeals and litigation. Not surprisingly, the map is quite complicated. Click here to review a larger version on the taxpayer advocate’s site.
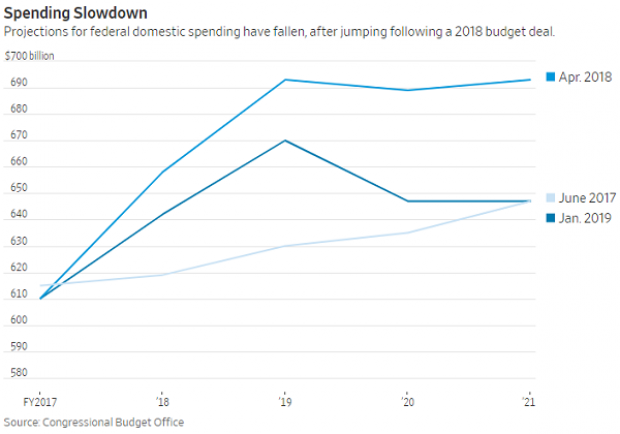
A Surprise Government Spending Slowdown

Economists expected federal spending to boost growth in 2019, but some of the fiscal stimulus provided by the 2018 budget deal has failed to show up this year, according to Kate Davidson of The Wall Street Journal.
Defense spending has come in as expected, but nondefense spending has lagged, and it’s unlikely to catch up to projections even if it accelerates in the coming months. Lower spending on disaster relief, the government shutdown earlier this year, and federal agencies spending less than they have been given by Congress all appear to be playing a role in the spending slowdown, Davidson said.
Number of the Day: $203,500

The Wall Street Journal’s Catherine Lucey reports that acting White House Chief of Staff Mick Mulvaney is making a bit more than his predecessors: “The latest annual report to Congress on White House personnel shows that President Trump’s third chief of staff is getting an annual salary of $203,500, compared with Reince Priebus and John Kelly, each of whom earned $179,700.” The difference is the result of Mulvaney still technically occupying the role of director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, where his salary level is set by law.
The White House told the Journal that if Mulvaney is made permanent chief of staff his salary would be adjusted to the current salary for an assistant to the president, $183,000.
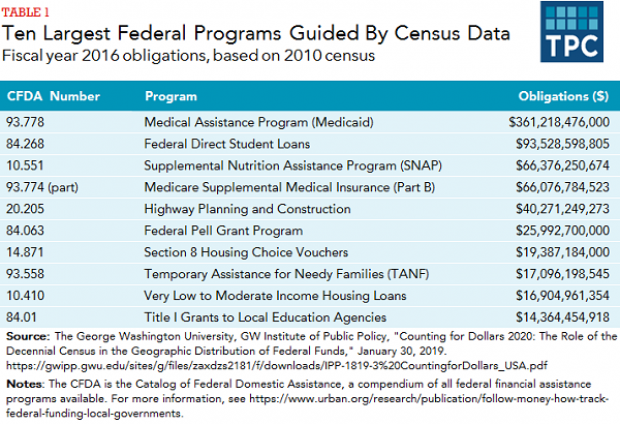
The Census Affects Nearly $1 Trillion in Spending

The 2020 census faces possible delay as the Supreme Court sorts out the legality of a controversial citizenship question added by the Trump administration. Tracy Gordon of the Tax Policy Center notes that in addition to the basic issue of political representation, the decennial population count affects roughly $900 billion in federal spending, ranging from Medicaid assistance funds to Section 8 housing vouchers. Here’s a look at the top 10 programs affected by the census:
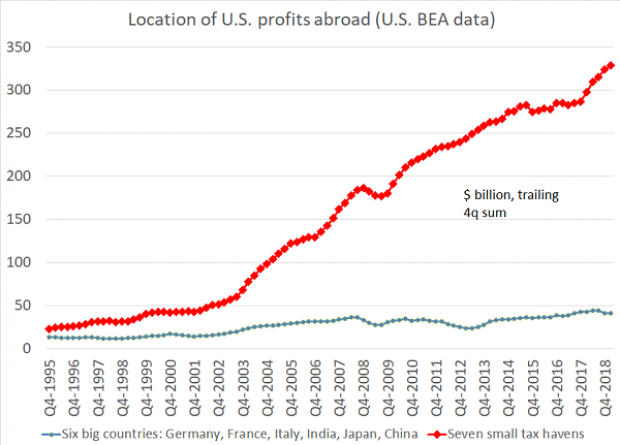
Chart of the Day: Offshore Profits Continue to Rise

Brad Setser, a former U.S. Treasury economist now with the Council on Foreign Relations, added another detail to his assessment of the foreign provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act: “A bit more evidence that Trump's tax reform didn't change incentives to offshore profits: the enormous profits that U.S. firms report in low tax jurisdictions continues to rise,” Setser wrote. “In fact, there was a bit of a jump up over the course of 2018.”