'Tax Reform Is Hard. Keeping Tax Reform Is Harder': Highlights from the House Tax Cuts Hearing

The House Ways and Means Committee held a three-hour hearing Wednesday on the effects of the Republican tax overhaul. We tuned in so you wouldn’t have to.
As you might have expected, the hearing was mostly an opportunity for Republicans and Democrats to exercise their messaging on the benefits or dangers of the new law, and for the experts testifying to disagree whether the gains from the law would outweigh the costs. But there was also some consensus that it’s still very early to try to gauge the effects of the law that was signed into effect by President Trump less than five months ago.
“I would emphasize that, despite all the high-quality economic research that’s been done, never before has the best economy on the planet moved from a worldwide system of taxation to a territorial system of taxation. There is no precedent,” said Douglas Holtz-Eakin, president of the American Action Forum and former director of the Congressional Budget Office. “And in that way we do not really know the magnitude and the pace at which a lot of these [effects] will occur.”
Some key quotes from the hearing:
Rep. Richard Neal (D-MA), ranking Democrat on the committee: “This was not tax reform. This was a tax cut for people at the top. The problem that Republicans hope Americans overlook is the law’s devastating impact on your health care. In search of revenue to pay for corporate cuts, the GOP upended the health care system, causing 13 million Americans to lose their coverage. For others, health insurance premiums will spike by at least 10 percent, which translates to about $2,000 a year of extra costs per year for a family of four. … These new health expenses will dwarf any tax cuts promised to American families. … The fiscal irresponsibility of their law is stunning. Over the next 10 years they add $2.3 trillion to the nation’s debt to finance tax cuts for people at the top – all borrowed money. … When the bill comes due, Republicans intend to cut funding for programs like Medicare, Medicaid and Social Security.”
David Farr, chairman and CEO of Emerson, and chairman of the National Association of Manufacturers: “We recently polled the NAM members, and the responses heard back from them on the tax reform are very significant and extremely positive: 86 percent report that they’ve already planned to increase investments, 77 percent report that they’ve already planned to increase hiring, 72 percent report that they’ve already planned to increase wages or benefits.”
Holtz-Eakin: “No, tax cuts don’t pay for themselves. If they did there would be no additional debt from the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, and there is. The question is, is it worth it? Will the growth and the incentives that come from it be worth the additional federal debt. My judgment on that was yes. Reasonable people can disagree. … When we went into this exercise, there was $10 trillion in debt in the federal baseline, before the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. There was a dangerous rise in the debt-to-GDP ratio. It was my belief, and continues to be my belief, that those problems would not be addressed in a stagnant, slow-growth economy. Those are enormously important problems, and we needed to get growth going so we can also take them on.”
“Quite frankly, it’s not going to be possible to hold onto this beneficial tax reform if you don’t get the spending side under control. Tax reform is hard. Keeping tax reform is harder, and the growth consequences of not fixing the debt outlook are entirely negative and will overwhelm what you’ve done so far.”
Steven Rattner: "We would probably all agree that increases in our national debt of these kinds of orders of magnitude have a number of deleterious effects. First, they push interest rates up. … That not only increases the cost of borrowing for the federal government, it increases the cost of borrowing for private corporations whose debt is priced off of government paper. Secondly, it creates additional pressure on spending inside the budget to the extent anyone is actually trying to control the deficit. … And thirdly, and in my view perhaps most importantly, it’s a terrible intergenerational transfer. We are simply leaving for our children additional trillions of dollars of debt that at some point are going to have to be dealt with, or there are going to have to be very, very substantial cuts in benefits, including programs like Social Security and Medicare, in order to reckon with that.”
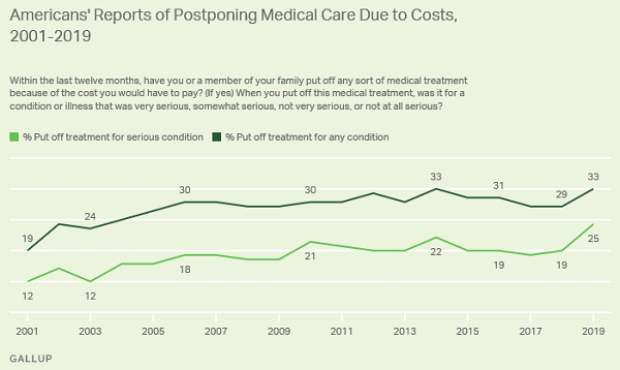
Increasing Number of Americans Delay Medical Care Due to Cost: Gallup

From Gallup: “A record 25% of Americans say they or a family member put off treatment for a serious medical condition in the past year because of the cost, up from 19% a year ago and the highest in Gallup's trend. Another 8% said they or a family member put off treatment for a less serious condition, bringing the total percentage of households delaying care due to costs to 33%, tying the high from 2014.”
Number of the Day: $213 Million

That’s how much the private debt collection program at the IRS collected in the 2019 fiscal year. In the black for the second year in a row, the program cleared nearly $148 million after commissions and administrative costs.
The controversial program, which empowers private firms to go after delinquent taxpayers, began in 2004 and ran for five years before the IRS ended it following a review. It was restarted in 2015 and ran at a loss for the next two years.
Senate Finance Chairman Chuck Grassley (R-IA), who played a central role in establishing the program, said Monday that the net proceeds are currently being used to hire 200 special compliance personnel at the IRS.
US Deficit Up 12% to $342 Billion for First Two Months of Fiscal 2020: CBO

The federal budget deficit for October and November was $342 billion, up $36 billion or 12% from the same period last year, the Congressional Budget Office estimated on Monday. Revenues were up 3% while outlays rose by 6%, CBO said.
Hospitals Sue to Protect Secret Prices

As expected, groups representing hospitals sued the Trump administration Wednesday to stop a new regulation would require them to make public the prices for services they negotiate with insurers. Claiming the rule “is unlawful, several times over,” the industry groups, which include the American Hospital Association, say the rule violates their First Amendment rights, among other issues.
"The burden of compliance with the rule is enormous, and way out of line with any projected benefits associated with the rule," the suit says. In response, a spokesperson for the Department of Health and Human Services said that hospitals “should be ashamed that they aren’t willing to provide American patients the cost of a service before they purchase it.”
See the lawsuit here, or read more at The New York Times.
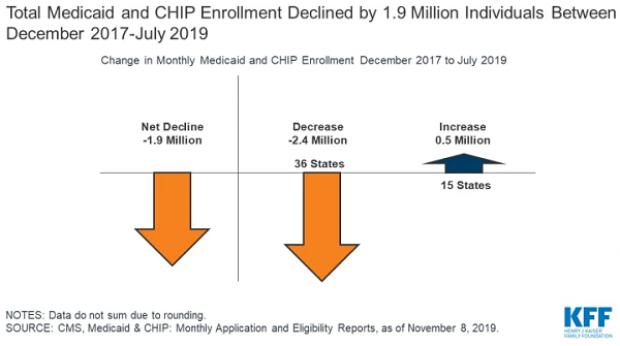
A Decline in Medicaid and CHIP Enrollment
Between December 2017 and July 2019, enrollment in Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) fell by 1.9 million, or 2.6%. The Kaiser Family Foundation provided an analysis of that drop Monday, saying that while some of it was likely caused by enrollees finding jobs that offer private insurance, a significant portion is related to enrollees losing health insurance of any kind. “Experiences in some states suggest that some eligible people may be losing coverage due to barriers maintaining coverage associated with renewal processes and periodic eligibility checks,” Kaiser said.