'Tax Reform Is Hard. Keeping Tax Reform Is Harder': Highlights from the House Tax Cuts Hearing

The House Ways and Means Committee held a three-hour hearing Wednesday on the effects of the Republican tax overhaul. We tuned in so you wouldn’t have to.
As you might have expected, the hearing was mostly an opportunity for Republicans and Democrats to exercise their messaging on the benefits or dangers of the new law, and for the experts testifying to disagree whether the gains from the law would outweigh the costs. But there was also some consensus that it’s still very early to try to gauge the effects of the law that was signed into effect by President Trump less than five months ago.
“I would emphasize that, despite all the high-quality economic research that’s been done, never before has the best economy on the planet moved from a worldwide system of taxation to a territorial system of taxation. There is no precedent,” said Douglas Holtz-Eakin, president of the American Action Forum and former director of the Congressional Budget Office. “And in that way we do not really know the magnitude and the pace at which a lot of these [effects] will occur.”
Some key quotes from the hearing:
Rep. Richard Neal (D-MA), ranking Democrat on the committee: “This was not tax reform. This was a tax cut for people at the top. The problem that Republicans hope Americans overlook is the law’s devastating impact on your health care. In search of revenue to pay for corporate cuts, the GOP upended the health care system, causing 13 million Americans to lose their coverage. For others, health insurance premiums will spike by at least 10 percent, which translates to about $2,000 a year of extra costs per year for a family of four. … These new health expenses will dwarf any tax cuts promised to American families. … The fiscal irresponsibility of their law is stunning. Over the next 10 years they add $2.3 trillion to the nation’s debt to finance tax cuts for people at the top – all borrowed money. … When the bill comes due, Republicans intend to cut funding for programs like Medicare, Medicaid and Social Security.”
David Farr, chairman and CEO of Emerson, and chairman of the National Association of Manufacturers: “We recently polled the NAM members, and the responses heard back from them on the tax reform are very significant and extremely positive: 86 percent report that they’ve already planned to increase investments, 77 percent report that they’ve already planned to increase hiring, 72 percent report that they’ve already planned to increase wages or benefits.”
Holtz-Eakin: “No, tax cuts don’t pay for themselves. If they did there would be no additional debt from the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, and there is. The question is, is it worth it? Will the growth and the incentives that come from it be worth the additional federal debt. My judgment on that was yes. Reasonable people can disagree. … When we went into this exercise, there was $10 trillion in debt in the federal baseline, before the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. There was a dangerous rise in the debt-to-GDP ratio. It was my belief, and continues to be my belief, that those problems would not be addressed in a stagnant, slow-growth economy. Those are enormously important problems, and we needed to get growth going so we can also take them on.”
“Quite frankly, it’s not going to be possible to hold onto this beneficial tax reform if you don’t get the spending side under control. Tax reform is hard. Keeping tax reform is harder, and the growth consequences of not fixing the debt outlook are entirely negative and will overwhelm what you’ve done so far.”
Steven Rattner: "We would probably all agree that increases in our national debt of these kinds of orders of magnitude have a number of deleterious effects. First, they push interest rates up. … That not only increases the cost of borrowing for the federal government, it increases the cost of borrowing for private corporations whose debt is priced off of government paper. Secondly, it creates additional pressure on spending inside the budget to the extent anyone is actually trying to control the deficit. … And thirdly, and in my view perhaps most importantly, it’s a terrible intergenerational transfer. We are simply leaving for our children additional trillions of dollars of debt that at some point are going to have to be dealt with, or there are going to have to be very, very substantial cuts in benefits, including programs like Social Security and Medicare, in order to reckon with that.”
Why Craft Brewers Are Crying in Their Beer

It may be small beer compared to the problems faced by unemployed federal workers and the growing cost for the overall economy, but the ongoing government shutdown is putting a serious crimp in the craft brewing industry. Small-batch brewers tend to produce new products on a regular basis, The Wall Street Journal’s Ruth Simon says, but each new formulation and product label needs to be approved by the Treasury Department’s Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau, which is currently closed. So it looks like you’ll have to wait a while to try the new version of Hemperor HPA from Colorado’s New Belgium Brewing, a hoppy brew that will include hemp seeds once the shutdown is over.
Number of the Day: $30 Billion
The amount spent on medical marketing reached $30 billion in 2016, up from $18 billion in 1997, according to a new analysis published in the Journal of the American Medical Association and highlighted by the Associated Press. The number of advertisements for prescription drugs appearing on television, newspapers, websites and elsewhere totaled 5 million in one year, accounting for $6 billion in marketing spending. Direct-to-consumer marketing grew the fastest, rising from $2 billion, or 12 percent of total marketing, to nearly $10 billion, or a third of spending. “Marketing drives more treatments, more testing” that patients don’t always need, Dr. Steven Woloshin, a Dartmouth College health policy expert and co-author of the study, told the AP.
70% of Registered Voters Want a Compromise to End the Shutdown

An overwhelming majority of registered voters say they want the president and Congress to “compromise to avoid prolonging the government shutdown” in a new The Hill-HarrisX poll. Seven in ten respondents said they preferred the parties reach some sort of deal to end the standoff, while 30 percent said it was more important to stick to principles, even if it means keeping parts of the government shutdown. Voters who “strongly approve” of Trump (a slim 21 percent of respondents) favored him sticking to his principles over the wall by a narrow 54 percent-46 percent margin. Voters who “somewhat approve” of the president favored a compromise solution by a 70-30 margin. Among Republicans overall, 61 percent said they wanted a compromise.
The survey of 1,000 registered voters was conducted January 5 and 6 and has a margin of error of 3.1 percentage points.
Share Buybacks Soar to Record $1 Trillion

Although there may be plenty of things in the GOP tax bill to complain about, critics can’t say it didn’t work – at least as far as stock buybacks go. TrimTabs Investment Research said Monday that U.S. companies have now announced $1 trillion in share buybacks in 2018, surpassing the record of $781 billion set in 2015. "It's no coincidence," said TrimTabs' David Santschi. "A lot of the buybacks are because of the tax law. Companies have more cash to pump up the stock price."
Chart of the Day: Deficits Rising
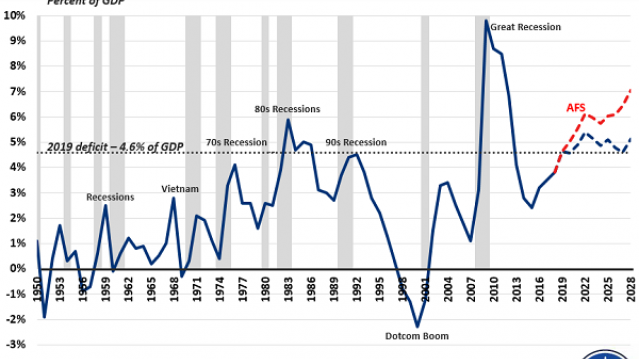
Budget deficits normally rise during recessions and fall when the economy is growing, but that’s not the case today. Deficits are rising sharply despite robust economic growth, increasing from $666 billion in 2017 to an estimated $970 billion in 2019, with $1 trillion annual deficits expected for years after that.
As the deficit hawks at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget point out in a blog post Thursday, “the deficit has never been this high when the economy was this strong … And never in modern U.S. history have deficits been so high outside of a war or recession (or their aftermath).” The chart above shows just how unusual the current deficit path is when measured as a percentage of GDP.
