Trump Clearly Has No Problem with Debt and Deficits

A self-proclaimed “king of debt,” President Trump has produced a budget that promises red ink as far as the eye can see. With last year's $1.5 trillion tax cut reducing revenues, the White House gave up even trying to pretend that its budget would balance anytime soon, and even the rosy economic projections contained in the budget couldn’t produce enough revenues, however fanciful, to cover the shortfall.
The Trump budget spends as much over 10 years as any budget produced by President Barack Obama, according to Jim Tankersley of The New York Times. And it projects total deficits of more than $7 trillion over the next decade — "a number that could double if the administration turns out to be overestimating economic growth and if the $3 trillion in spending cuts the White House has floated do not materialize in Congress,” Tankersley says.
Trump — who once promised to both balance the budget and pay down the national debt — isn’t the only one throwing off the shackles of fiscal restraint. Republicans as a whole appear to be embracing a new set of economic preferences defined by lower taxes and higher spending, in what Bloomberg describes as a “striking turnabout” in attitudes toward deficits and the national debt.
But some conservatives tell Tankersley that the GOP's core beliefs on spending and debt remain intact — and that spending on Social Security and Medicare, the primary drivers of the national debt, are all that matters when it comes to implementing fiscal restraint.
“They know that right now, a fundamental reform of entitlements won’t happen," John H. Cochrane, an economist at Stanford University’s Hoover Institution, tells Tankersley. "So, they have avoided weekly chaos and gotten needed military spending through by opening the spending bill, and they got an important reduction in growth-distorting marginal corporate rates through by accepting a bit more deficits. They know that can’t be the end of the story.”
Democrats, of course, have warned that the next chapter in the tale will involve big cuts to Social Security and Medicare. Even before we get there, though, Tankersley questions whether the GOP approach stands up to scrutiny: "This is a bit like saying, only regular exercise will keep America from having a fatal heart attack, so, you know, it's ok to eat a few more hamburgers now."
Tweet of the Day: The Black Hole of Big Pharma
Billionaire John D. Arnold, a former energy trader and hedge fund manager turned philanthropist with a focus on health care, says Big Pharma appears to have a powerful hold on members of Congress.
Arnold pointed out that PhRMA, the main pharmaceutical industry lobbying group, had revenues of $459 million in 2018, and that total lobbying on behalf of the sector probably came to about $1 billion last year. “I guess $1 bil each year is an intractable force in our political system,” he concluded.
Warren’s Taxes Could Add Up to More Than 100%

The Wall Street Journal’s Richard Rubin says Elizabeth Warren’s proposed taxes could claim more than 100% of income for some wealthy investors. Here’s an example Rubin discussed Friday:
“Consider a billionaire with a $1,000 investment who earns a 6% return, or $60, received as a capital gain, dividend or interest. If all of Ms. Warren’s taxes are implemented, he could owe 58.2% of that, or $35 in federal tax. Plus, his entire investment would incur a 6% wealth tax, i.e., at least $60. The result: taxes as high as $95 on income of $60 for a combined tax rate of 158%.”
In Rubin’s back-of-the-envelope analysis, an investor worth $2 billion would need to achieve a return of more than 10% in order to see any net gain after taxes. Rubin notes that actual tax bills would likely vary considerably depending on things like location, rates of return, and as-yet-undefined policy details. But tax rates exceeding 100% would not be unusual, especially for billionaires.
Biden Proposes $1.3 Trillion Infrastructure Plan

Joe Biden on Thursday put out a $1.3 trillion infrastructure proposal. The 10-year “Plan to Invest in Middle Class Competitiveness” calls for investments to revitalize the nation’s roads, highways and bridges, speed the adoption of electric vehicles, launch a “second great railroad revolution” and make U.S. airports the best in the world.
“The infrastructure plan Joe Biden released Thursday morning is heavy on high-speed rail, transit, biking and other items that Barack Obama championed during his presidency — along with a complete lack of specifics on how he plans to pay for it all,” Politico’s Tanya Snyder wrote. Biden’s campaign site says that every cent of the $1.3 trillion would be paid for by reversing the 2017 corporate tax cuts, closing tax loopholes, cracking down on tax evasion and ending fossil-fuel subsidies.
Read more about Biden’s plan at Politico.
Number of the Day: 18 Million

There were 18 million military veterans in the United States in 2018, according to the Census Bureau. That figure includes 485,000 World War II vets, 1.3 million who served in the Korean War, 6.4 million from the Vietnam War era, 3.8 million from the first Gulf War and another 3.8 million since 9/11. We join with the rest of the country today in thanking them for their service.
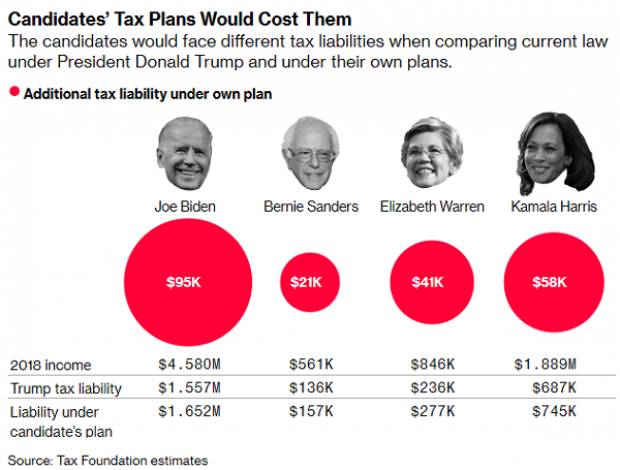
Chart of the Day: Dem Candidates Face Their Own Tax Plans

Democratic presidential candidates are proposing a variety of new taxes to pay for their preferred social programs. Bloomberg’s Laura Davison and Misyrlena Egkolfopoulou took a look at how the top four candidates would fare under their own tax proposals.