Automakers Are Having a Record Year, but Here’s a Trend that Should Worry Them

U.S. auto sales closed out the summer on a positive note, topping estimates and casting some rosy light on the health of the American consumer. Recording its best August since 2003, the auto industry is on pace to sell 17.8 vehicles in 2015, well ahead of expectations of 17.3 million. If the numbers hold up, 2015 will be the best year ever for U.S. auto sales, beating the 17.4 million mark set in 2000.
The general consensus is that auto industry is in pretty good shape these days. Gas prices and interest rates are low, boosting the market for cars and light trucks. More than 2 million jobs were added to the U.S. economy in the past year, and more jobs is usually good news for auto sales. The unemployment rate has been trending lower for five years, sitting at a relatively healthy 5.3 percent in July.
Related: What's Next for Oil Prices? Look Out Below!
As with any statistic, though, there’s more than one way to look at the situation. Sure, auto sales are climbing as the economy gets stronger and more Americans hit their local car dealers’ lots. At least to some degree, though, higher auto sales should be expected just as a result of U.S. population growth. And those rising monthly sales figures are masking a continuing trend that is more worrisome for the auto industry: per capita auto sales are still in a long-term decline, even including the solid growth the industry has seen since the end of the recession. Doug Short at Advisor Perspectives did the math and made a graph:

According to Short’s analysis, the peak year for per capita auto sales in the U.S. was 1978. As the red line in the graph shows, the trend is negative since then.
In the graph, per capita auto sales in January, 1976, were defined as 100; the readings in the index since then are relative to that 1976 sales level. As you can see, the index moves higher until August of 1978, when per capita auto sales were up nearly 20 percent over 1976. Since then, per capita auto sales have fallen, reaching a low in 2009 that was nearly 50 percent lower than 1976. Since 2009, per capita auto sales have risen nicely, but are still more than 15 percent below peak.
What could explain the negative trend? Two factors come to mind. First, demographics. It has been widely reported that the millennial generation is less interested in owning cars for a variety of reasons, ranging from a weak economy to a cultural shift away from suburban life. However, the data on millennial car purchases is ambiguous; recently, millennials have started buying cars in volumes that look a lot like their elders. And even if millennials are less interested in buying cars, their preferences can’t explain a shift that began in the 1970s, before they were born.
Related: U.S. Companies Are Dying Faster Than Ever
The other factor that may explain the trend is income inequality. A study of car ownership by the Carnegie Foundation found that countries with higher income inequality have fewer cars per capita. The logic is simple: As more income is claimed by the wealthy, there’s less to go around for everyone else. And that means there’s less money for middle and lower income groups to buy and maintain automobiles, among other things.
Here’s a chart of the Gini index for the U.S. since 1947. (The Gini Index is a widely-used measure of income inequality. A higher Gini number means higher inequality.) Note that the Gini reading started climbing in the late ‘70s – the same time when per capita car ownership in the U.S. began to fall.
This chart tells us, not for the first time, that the U.S. has experienced more income inequality since the 1970s. Combined with the per capita auto sales data above, it suggests that as the rich have gotten richer and everyone else has struggled to keep up, car ownership has suffered. Although this is by no means proof of the relationship between income inequality and per capita car ownership over the last 40 years, it hints at an interesting theory – and suggests that the auto industry has good reason to be concerned about growing inequality in the U.S.

Top Reads From The Fiscal Times:
- 6 Reasons Gas Prices Could Fall Below $2 a Gallon
- Hoping for a Raise? Here’s How Much Most People Are Getting
- What the U.S. Must Do to Avoid Another Financial Crisis
Tweet of the Day: The Black Hole of Big Pharma
Billionaire John D. Arnold, a former energy trader and hedge fund manager turned philanthropist with a focus on health care, says Big Pharma appears to have a powerful hold on members of Congress.
Arnold pointed out that PhRMA, the main pharmaceutical industry lobbying group, had revenues of $459 million in 2018, and that total lobbying on behalf of the sector probably came to about $1 billion last year. “I guess $1 bil each year is an intractable force in our political system,” he concluded.
Warren’s Taxes Could Add Up to More Than 100%

The Wall Street Journal’s Richard Rubin says Elizabeth Warren’s proposed taxes could claim more than 100% of income for some wealthy investors. Here’s an example Rubin discussed Friday:
“Consider a billionaire with a $1,000 investment who earns a 6% return, or $60, received as a capital gain, dividend or interest. If all of Ms. Warren’s taxes are implemented, he could owe 58.2% of that, or $35 in federal tax. Plus, his entire investment would incur a 6% wealth tax, i.e., at least $60. The result: taxes as high as $95 on income of $60 for a combined tax rate of 158%.”
In Rubin’s back-of-the-envelope analysis, an investor worth $2 billion would need to achieve a return of more than 10% in order to see any net gain after taxes. Rubin notes that actual tax bills would likely vary considerably depending on things like location, rates of return, and as-yet-undefined policy details. But tax rates exceeding 100% would not be unusual, especially for billionaires.
Biden Proposes $1.3 Trillion Infrastructure Plan

Joe Biden on Thursday put out a $1.3 trillion infrastructure proposal. The 10-year “Plan to Invest in Middle Class Competitiveness” calls for investments to revitalize the nation’s roads, highways and bridges, speed the adoption of electric vehicles, launch a “second great railroad revolution” and make U.S. airports the best in the world.
“The infrastructure plan Joe Biden released Thursday morning is heavy on high-speed rail, transit, biking and other items that Barack Obama championed during his presidency — along with a complete lack of specifics on how he plans to pay for it all,” Politico’s Tanya Snyder wrote. Biden’s campaign site says that every cent of the $1.3 trillion would be paid for by reversing the 2017 corporate tax cuts, closing tax loopholes, cracking down on tax evasion and ending fossil-fuel subsidies.
Read more about Biden’s plan at Politico.
Number of the Day: 18 Million

There were 18 million military veterans in the United States in 2018, according to the Census Bureau. That figure includes 485,000 World War II vets, 1.3 million who served in the Korean War, 6.4 million from the Vietnam War era, 3.8 million from the first Gulf War and another 3.8 million since 9/11. We join with the rest of the country today in thanking them for their service.
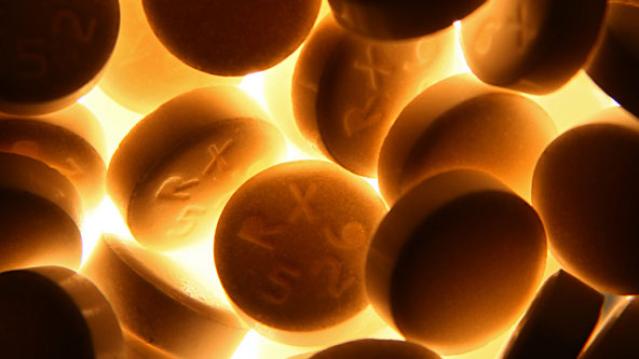
Chart of the Day: Dem Candidates Face Their Own Tax Plans

Democratic presidential candidates are proposing a variety of new taxes to pay for their preferred social programs. Bloomberg’s Laura Davison and Misyrlena Egkolfopoulou took a look at how the top four candidates would fare under their own tax proposals.