Why Big Salary Raises May Be Gone for Good

If you’re hoping for a big raise this year, prepare to be disappointed. Sure, you might be among the lucky people who get a healthy bump in salary, but a recent survey by professional services firm Towers Watson found that companies are planning pay raises of 3 percent on average for workers.
A new survey by human resources and management consultancy Aon Hewitt confirms that forecast: Even as the job market continues to improve, salaried employees can expect their base pay to increase 3 percent, or about a percentage point smaller than the raises employers were handing out 20 years ago.
Related: Full Employment Alone Won’t Solve Problem of Stagnating Wages
From 1996 through 2000, salaries went up by about 4.1 percent a year, according to Aon Hewitt data. From 2011 through 2015, annual raises have averaged about 2.8 percent. And even as we get further away from the recession, that downward shift appears to be permanent, as companies look to keep a lid on their fixed costs.
"The modest increases we've seen over the past 20 years are an indication that employers have changed their compensation strategies for good, and we shouldn't expect to see salary increases revert back to 4 percent or higher levels that were commonplace in the past," said Aon Hewitt’s Ken Abosch.
Related: Obama Moves Toward Executive Action on Overtime Pay
On the bright side, at least for some workers, employers are planning on doling out more money in the form of bonuses, cash awards and other so-called variable pay. Aon Hewitt’s survey found that workers will see their variable pay rise by 12.9 percent this year.
That shift favors higher-level white-collar workers, since companies have been cutting back on bonus and incentive pay for clerical or technical workers. In 2011, only 43 percent of companies gave bonuses or other cash incentives to those hourly workers eligible for overtime pay, down from 61 percent in 2009, according to data Aon Hewitt shared with The Washington Post. On the other hand, 93 percent of companies offer incentive programs to employees with a fixed salary.
As Abosch told the Post: “It’s the haves and the have nots.”
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times
- How a Biden-Warren Ticket Could Transform the Campaign
- The 10 Best States for Property Taxes
- Air Force Brushes off $27 Billion Accounting Error
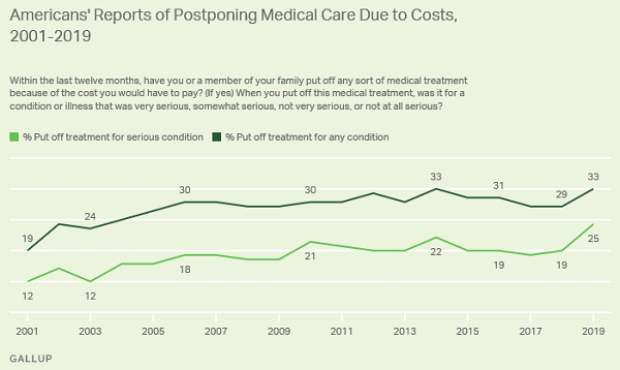
Increasing Number of Americans Delay Medical Care Due to Cost: Gallup

From Gallup: “A record 25% of Americans say they or a family member put off treatment for a serious medical condition in the past year because of the cost, up from 19% a year ago and the highest in Gallup's trend. Another 8% said they or a family member put off treatment for a less serious condition, bringing the total percentage of households delaying care due to costs to 33%, tying the high from 2014.”
Number of the Day: $213 Million

That’s how much the private debt collection program at the IRS collected in the 2019 fiscal year. In the black for the second year in a row, the program cleared nearly $148 million after commissions and administrative costs.
The controversial program, which empowers private firms to go after delinquent taxpayers, began in 2004 and ran for five years before the IRS ended it following a review. It was restarted in 2015 and ran at a loss for the next two years.
Senate Finance Chairman Chuck Grassley (R-IA), who played a central role in establishing the program, said Monday that the net proceeds are currently being used to hire 200 special compliance personnel at the IRS.
US Deficit Up 12% to $342 Billion for First Two Months of Fiscal 2020: CBO

The federal budget deficit for October and November was $342 billion, up $36 billion or 12% from the same period last year, the Congressional Budget Office estimated on Monday. Revenues were up 3% while outlays rose by 6%, CBO said.
Hospitals Sue to Protect Secret Prices

As expected, groups representing hospitals sued the Trump administration Wednesday to stop a new regulation would require them to make public the prices for services they negotiate with insurers. Claiming the rule “is unlawful, several times over,” the industry groups, which include the American Hospital Association, say the rule violates their First Amendment rights, among other issues.
"The burden of compliance with the rule is enormous, and way out of line with any projected benefits associated with the rule," the suit says. In response, a spokesperson for the Department of Health and Human Services said that hospitals “should be ashamed that they aren’t willing to provide American patients the cost of a service before they purchase it.”
See the lawsuit here, or read more at The New York Times.
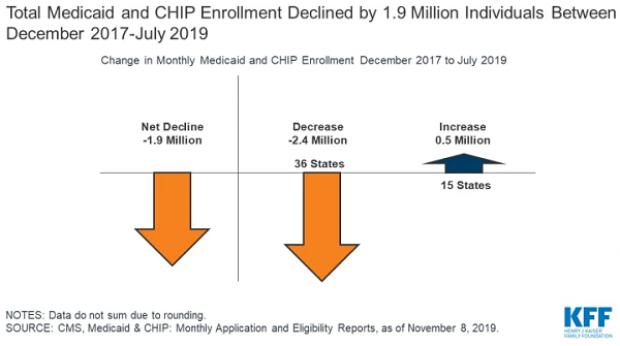
A Decline in Medicaid and CHIP Enrollment
Between December 2017 and July 2019, enrollment in Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) fell by 1.9 million, or 2.6%. The Kaiser Family Foundation provided an analysis of that drop Monday, saying that while some of it was likely caused by enrollees finding jobs that offer private insurance, a significant portion is related to enrollees losing health insurance of any kind. “Experiences in some states suggest that some eligible people may be losing coverage due to barriers maintaining coverage associated with renewal processes and periodic eligibility checks,” Kaiser said.