Why Big Salary Raises May Be Gone for Good

If you’re hoping for a big raise this year, prepare to be disappointed. Sure, you might be among the lucky people who get a healthy bump in salary, but a recent survey by professional services firm Towers Watson found that companies are planning pay raises of 3 percent on average for workers.
A new survey by human resources and management consultancy Aon Hewitt confirms that forecast: Even as the job market continues to improve, salaried employees can expect their base pay to increase 3 percent, or about a percentage point smaller than the raises employers were handing out 20 years ago.
Related: Full Employment Alone Won’t Solve Problem of Stagnating Wages
From 1996 through 2000, salaries went up by about 4.1 percent a year, according to Aon Hewitt data. From 2011 through 2015, annual raises have averaged about 2.8 percent. And even as we get further away from the recession, that downward shift appears to be permanent, as companies look to keep a lid on their fixed costs.
"The modest increases we've seen over the past 20 years are an indication that employers have changed their compensation strategies for good, and we shouldn't expect to see salary increases revert back to 4 percent or higher levels that were commonplace in the past," said Aon Hewitt’s Ken Abosch.
Related: Obama Moves Toward Executive Action on Overtime Pay
On the bright side, at least for some workers, employers are planning on doling out more money in the form of bonuses, cash awards and other so-called variable pay. Aon Hewitt’s survey found that workers will see their variable pay rise by 12.9 percent this year.
That shift favors higher-level white-collar workers, since companies have been cutting back on bonus and incentive pay for clerical or technical workers. In 2011, only 43 percent of companies gave bonuses or other cash incentives to those hourly workers eligible for overtime pay, down from 61 percent in 2009, according to data Aon Hewitt shared with The Washington Post. On the other hand, 93 percent of companies offer incentive programs to employees with a fixed salary.
As Abosch told the Post: “It’s the haves and the have nots.”
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times
- How a Biden-Warren Ticket Could Transform the Campaign
- The 10 Best States for Property Taxes
- Air Force Brushes off $27 Billion Accounting Error
Stat of the Day: 0.2%

The New York Times’ Jim Tankersley tweets: “In order to raise enough revenue to start paying down the debt, Trump would need tariffs to be ~4% of GDP. They're currently 0.2%.”
Read Tankersley’s full breakdown of why tariffs won’t come close to eliminating the deficit or paying down the national debt here.
Number of the Day: 44%

The “short-term” health plans the Trump administration is promoting as low-cost alternatives to Obamacare aren’t bound by the Affordable Care Act’s requirement to spend a substantial majority of their premium revenues on medical care. UnitedHealth is the largest seller of short-term plans, according to Axios, which provided this interesting detail on just how profitable this type of insurance can be: “United’s short-term plans paid out 44% of their premium revenues last year for medical care. ACA plans have to pay out at least 80%.”
Number of the Day: 4,229

The Washington Post’s Fact Checkers on Wednesday updated their database of false and misleading claims made by President Trump: “As of day 558, he’s made 4,229 Trumpian claims — an increase of 978 in just two months.”
The tally, which works out to an average of almost 7.6 false or misleading claims a day, includes 432 problematics statements on trade and 336 claims on taxes. “Eighty-eight times, he has made the false assertion that he passed the biggest tax cut in U.S. history,” the Post says.
Number of the Day: $3 Billion

A new analysis by the Department of Health and Human Services finds that Medicare’s prescription drug program could have saved almost $3 billion in 2016 if pharmacies dispensed generic drugs instead of their brand-name counterparts, Axios reports. “But the savings total is inflated a bit, which HHS admits, because it doesn’t include rebates that brand-name drug makers give to [pharmacy benefit managers] and health plans — and PBMs are known to play games with generic drugs to juice their profits.”
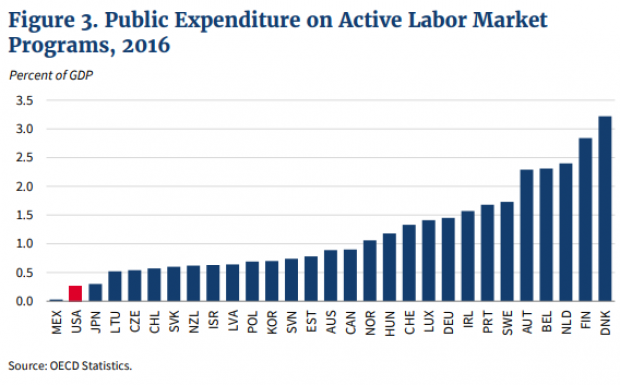
Chart of the Day: Public Spending on Job Programs

President Trump announced on Thursday the creation of a National Council for the American Worker, charged with developing “a national strategy for training and retraining workers for high-demand industries,” his daughter Ivanka wrote in The Wall Street Journal. A report from the president’s National Council on Economic Advisers earlier this week made it clear that the U.S. currently spends less public money on job programs than many other developed countries.