You Won’t Believe How Much Diabetes is Costing the U.S.
The budget-busting price of Sovaldi, a drug used to treat hepatitis C has generated wave after wave of media attention, but it’s far from the only drug creating cost problems for patients and insurers.
As Michelle Andrews of Kaiser Health News points out, diabetes affects 29 million Americans, or 10 times as many people as hepatitis C, and the costs of treating it have been rising quickly. And because it’s a chronic condition, people require lifetime care.
Related: Diabetes Detection Up in Pro-Obamacare States
In 2011, the average annual health spending for individuals with diabetes was $14,093. Two years later, it had risen to $14,999, according to the Healthcare Cost Institute. In contrast, a person without diabetes spent about $10,000 less in medical costs in 2013. Pharmacy provider Express Scripts said earlier this year that 2014 marked the fourth year in a row that medication used to treat diabetes were the most expensive of any traditional drug class.
In all, diabetes costs totaled an estimated $245 billion in 2012, including both direct medical expenses and indirect costs from disability and lost work productivity.
While some of the most popular diabetes drugs aren’t particularly expensive, the new brand-name drugs that are continually being introduced offer more effective treatment and fewer side effects — but also come with a higher price tag. Less than half of the diabetes prescription treatments filled in 2014 were generic.
Nearly a century after its discovery in 1921, insulin is still a common form of treatment for the millions of people with type 1 diabetes, yet there is still no generic form available. Patent protection has been extended in some cases due to improvements in existing formulations. Once those patents expire, Andrews notes, biologically similar drugs could replace them and reduce the price by up to 40 percent.
Related: This Disease Hikes Health Care Costs By More than $10,000 a Year
The financial ramifications of diabetes don’t just stem from the cost of drugs or medical treatment — it’s also been proven that people with diabetes have a high-school dropout rate that is six percentage points higher than those without the disease, according to a Health Affairs study. In addition, young adults with diabetes are four to six percentage points less likely to attend college than those without the disease.
Diabetes also contributes to lower employment and wages. On average, a person with diabetes earns $160,000 less over the course of their lives than people who don’t develop the disease. By age 30, a person with diabetes is 10 percent less likely to be employed.
So even if it’s not generating as many headlines as hepatitis C at any given point in time, the costs of diabetes can’t be ignored.
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times
- The 10 Worst States for Property Taxes
- Two-Thirds of Americans Believe Social Security Is in a Crisis State
- Why McDonald’s Could Suddenly Be Responsible for Millions of New Employees
Deficit Hits $738.6 Billion in First 8 Months of Fiscal Year

The U.S. budget deficit grew to $738.6 billion in the first eight months of the current fiscal year – an increase of $206 billion, or 38.8%, over the deficit recorded during the same period a year earlier. Bloomberg’s Sarah McGregor notes that the big increase occurred despite a jump in tariff revenues, which have nearly doubled to $44.9 billion so far this fiscal year. But that increase, which contributed to an overall increase in revenues of 2.3%, was not enough to make up for the reduced revenues from the Republican tax cuts and a 9.3% increase in government spending.
Tweet of the Day: Revenues or Spending?

Rep. Kevin Brady (R-TX), ranking member of the House Ways and Means Committee and one of the authors of the 2017 Republican tax overhaul, told The Washington Post’s Heather Long Tuesday that the budget deficit is driven by excess spending, not a shortfall in revenues in the wake of the tax cuts. The Wall Street Journal’s Kate Davidson provided some inconvenient facts for Brady’s claim in a tweet, pointing out that government revenues as a share of GDP have fallen significantly since 2015, while spending has remained more or less constant.
Chart of the Day: The Decline in IRS Audits

Reviewing the recent annual report on tax statistics from the IRS, Robert Weinberger of the Tax Policy Center says it “tells a story of shrinking staff, fewer audits, and less customer service.” The agency had 22% fewer personnel in 2018 than it did in 2010, and its enforcement budget has fallen by nearly $1 billion, Weinberger writes. One obvious effect of the budget cuts has been a sharp reduction in the number of audits the agency has performed annually, which you can see in the chart below.
Number of the Day: $102 Million

President Trump’s golf playing has cost taxpayers $102 million in extra travel and security expenses, according to an analysis by the left-leaning HuffPost news site.
“The $102 million total to date spent on Trump’s presidential golfing represents 255 times the annual presidential salary he volunteered not to take. It is more than three times the cost of special counsel Robert Mueller’s investigation that Trump continually complains about. It would fund for six years the Special Olympics program that Trump’s proposed budget had originally cut to save money,” HuffPost’s S.V. Date writes.
Date says the White House did not respond to HuffPost’s requests for comment.
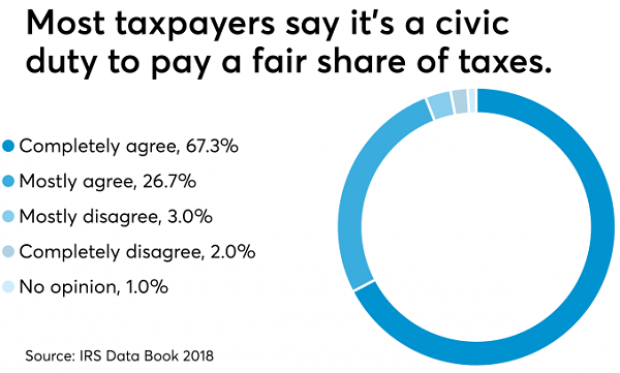
Americans See Tax-Paying as a Duty

The IRS may not be conducting audits like it used to, but according to the agency’s Data Book for 2018, most Americans still believe it’s not acceptable to cheat on your taxes. About 67% of respondents to an IRS opinion survey “completely agree” that it’s a civic duty to pay “a fair share of taxes,” and another 26% “mostly agree,” bringing the total in agreement to over 90%. Accounting Today says that attitude has been pretty consistent over the last decade.