The Amount of Money Lost to Ad-Blocking Is Skyrocketing

Are you annoyed by online pop-up ads or those video commercials that automatically start playing when you visit a new Web page? Worried about advertisers collecting your personal information online? You’re not alone. In the perpetual cat and mouse game between marketers and Internet users, the utilization of ad-blocking software by Web surfers is growing rapidly — and it’s costing advertisers billions.
Ad-blocking technology was employed by 45 million active users during the second quarter of 2015, a new report by PageFair and Adobe found. This represents 16 percent of the U.S. online population. In the past year, the number of users blocking ads grew by 48 percent.
In 2014, ad-blocking in the U.S. cost an estimated $5.8 billion in lost advertising revenue. That figure is expected to jump to $10.7 billion in 2015 and $20.3 billion in 2016 as more users adopt the practice. The new version of Apple’s mobile operating system coming this fall is expected to make the problem worse, since it will allow iPhone users to block ads in Safari with a simple app.
In addition to lost revenue, ad-blocking skews the demographics of the online audience. Websites that cater to younger users — a demographic advertisers are eager to target — are the ones most significantly affected by ad-blocking.
Related: The Future of Advertising: Everything, Everywhere, All the Time
A survey in the PageFair/Adobe report found that the main reason individuals block ads is a concern about advertisers mishandling personal data.
Advertisers have a long way to go when it comes to trust. An article in AdAge argues that marketers should be more transparent about the ways they use the information they collect. It recommends giving users more control of their personal data, the ability to decide how much information to share and the choice to opt-out at any time.
Trust isn’t the only issue, though. The appeal of ad-blocking is growing as “malvertising” attacks become more common. Last month, Yahoo’s ad network was targeted for seven days by hackers who sent out corrupt bits of code through Flash-based ads to visitors on Yahoo’s popular sites. Some users were redirected to sites that paid the hackers for traffic, while others had their computers locked for ransom.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- Bush Looks to Make Up for Past Blunders on Iraq Policy
- Oil Sector Insiders Signal It’s Time to Buy
- How a Soaring Dollar Forced China to Devalue Its Currency
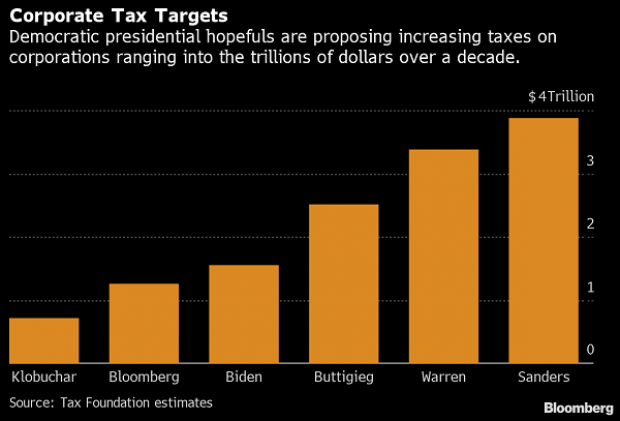
Chart of the Day: Boosting Corporate Tax Revenues

The leading candidates for the Democratic presidential nomination have all proposed increasing taxes on corporations, including raising income tax rates to levels ranging from 25% to 35%, up from the current 21% imposed by the Republican tax cuts in 2017. With Bernie Sanders leading the way at $3.9 trillion, here’s how much revenue the higher proposed corporate taxes, along with additional proposed surtaxes and reduced tax breaks, would generate over a decade, according to calculations by the right-leaning Tax Foundation, highlighted Wednesday by Bloomberg News.
Chart of the Day: Discretionary Spending Droops
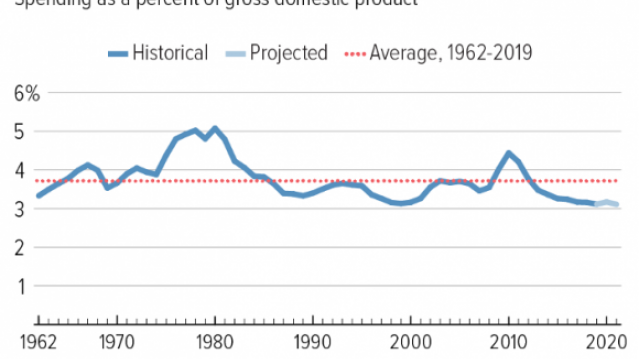
The federal government’s total non-defense discretionary spending – which covers everything from education and national parks to veterans’ medical care and low-income housing assistance – equals 3.2% of GDP in 2020, near historic lows going back to 1962, according to an analysis this week from the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Chart of the Week: Trump Adds $4.7 Trillion in Debt
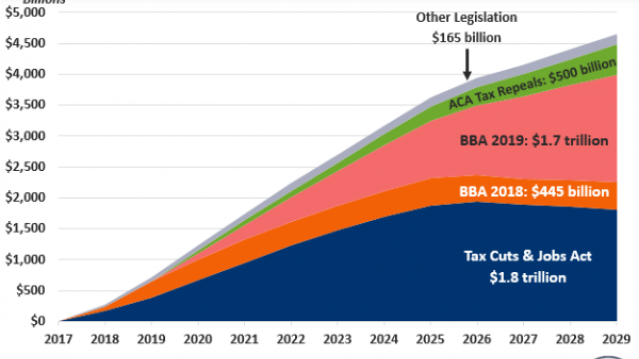
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget estimated this week that President Trump has now signed legislation that will add a total of $4.7 trillion to the national debt between 2017 and 2029. Tax cuts and spending increases account for similar portions of the projected increase, though if the individual tax cuts in the 2017 Republican overhaul are extended beyond their current expiration date at the end of 2025, they would add another $1 trillion in debt through 2029.
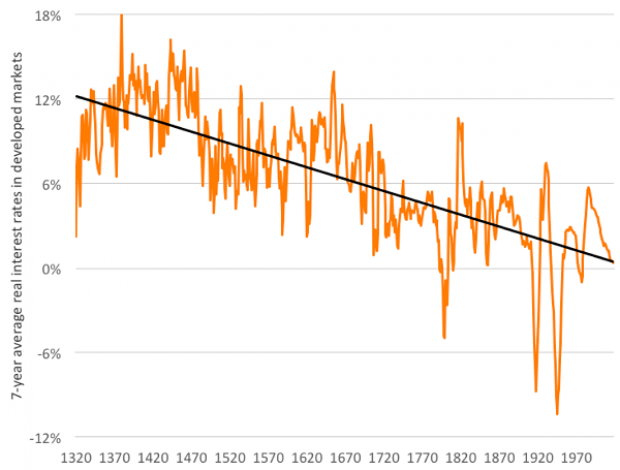
Chart of the Day: The Long Decline in Interest Rates
Are interest rates destined to move higher, increasing the cost of private and public debt? While many experts believe that higher rates are all but inevitable, historian Paul Schmelzing argues that today’s low-interest environment is consistent with a long-term trend stretching back 600 years.
The chart “shows a clear historical downtrend, with rates falling about 1% every 60 years to near zero today,” says Bloomberg’s Aaron Brown. “Rates do tend to revert to a mean, but that mean seems to be declining.”
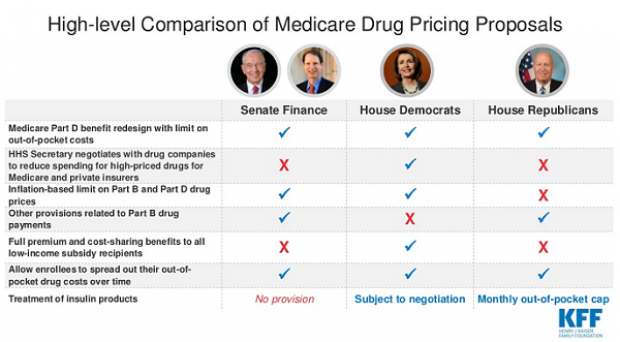
Chart of the Day: Drug Price Plans Compared
Lawmakers are considering three separate bills that are intended to reduce the cost of prescription drugs. Here’s an overview of the proposals, from a series of charts produced by the Kaiser Family Foundation this week. An interesting detail highlighted in another chart: 88% of voters – including 92% of Democrats and 85% of Republicans – want to give the government the power to negotiate prices with drug companies.