Meet Blade, the Uber for Helicopters in NYC

Uber may be convenient, but New York’s Hamptons set doesn’t always have the time or patience to deal with the traffic getting out to their summer spots on Long Island’s East End.
Blade, which calls itself “the first digitally driven short distance aviation company,” says it has a solution for those who want to get to East Hampton within the hour, or Southampton in 35 minutes: Ordering their own chartered helicopter via an app.
Related: 10 Biggest Tech Flops of the Century
Once you download the app, you can select your flight time, chill out in a Blade lounge at a Manhattan heliport and then enjoy “a snack, a drink, a newspaper and lots of other fun things” on your flight. Passengers are allowed one carry-on weighing 25 lbs. maximum — but no golf clubs.
The service, which launched in May 2014, doesn’t come cheap, at $595 per seat to go to Quogue, Southampton, East Hampton, Montauk or Fire Island. Blade can also be booked for trips to Nantucket, Martha’s Vineyard, Cape Cod and some other destinations in the Northeast as well as to the New York area’s major airports.
The website advises that if your flight is grounded due to bad weather, you’ll be offered a ride to your destination in a chauffeured Mercedes at no extra cost.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- The Best Things to Charge on Your Credit Card
- The Wealthy Worry, Too—And It’s Not All About Money
- 10 Best Islands in the World
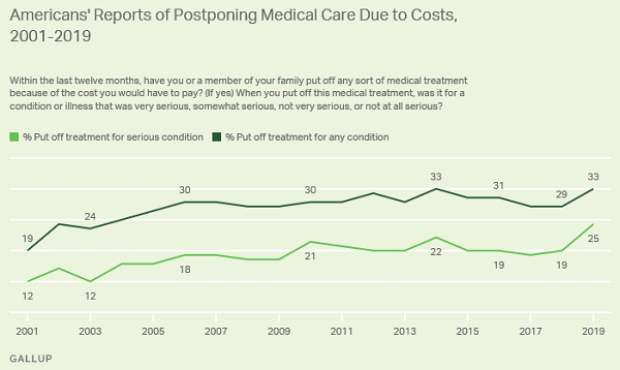
Increasing Number of Americans Delay Medical Care Due to Cost: Gallup

From Gallup: “A record 25% of Americans say they or a family member put off treatment for a serious medical condition in the past year because of the cost, up from 19% a year ago and the highest in Gallup's trend. Another 8% said they or a family member put off treatment for a less serious condition, bringing the total percentage of households delaying care due to costs to 33%, tying the high from 2014.”
Number of the Day: $213 Million

That’s how much the private debt collection program at the IRS collected in the 2019 fiscal year. In the black for the second year in a row, the program cleared nearly $148 million after commissions and administrative costs.
The controversial program, which empowers private firms to go after delinquent taxpayers, began in 2004 and ran for five years before the IRS ended it following a review. It was restarted in 2015 and ran at a loss for the next two years.
Senate Finance Chairman Chuck Grassley (R-IA), who played a central role in establishing the program, said Monday that the net proceeds are currently being used to hire 200 special compliance personnel at the IRS.
US Deficit Up 12% to $342 Billion for First Two Months of Fiscal 2020: CBO

The federal budget deficit for October and November was $342 billion, up $36 billion or 12% from the same period last year, the Congressional Budget Office estimated on Monday. Revenues were up 3% while outlays rose by 6%, CBO said.
Hospitals Sue to Protect Secret Prices

As expected, groups representing hospitals sued the Trump administration Wednesday to stop a new regulation would require them to make public the prices for services they negotiate with insurers. Claiming the rule “is unlawful, several times over,” the industry groups, which include the American Hospital Association, say the rule violates their First Amendment rights, among other issues.
"The burden of compliance with the rule is enormous, and way out of line with any projected benefits associated with the rule," the suit says. In response, a spokesperson for the Department of Health and Human Services said that hospitals “should be ashamed that they aren’t willing to provide American patients the cost of a service before they purchase it.”
See the lawsuit here, or read more at The New York Times.
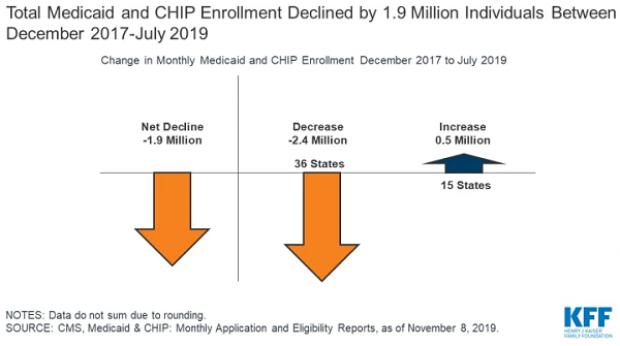
A Decline in Medicaid and CHIP Enrollment
Between December 2017 and July 2019, enrollment in Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) fell by 1.9 million, or 2.6%. The Kaiser Family Foundation provided an analysis of that drop Monday, saying that while some of it was likely caused by enrollees finding jobs that offer private insurance, a significant portion is related to enrollees losing health insurance of any kind. “Experiences in some states suggest that some eligible people may be losing coverage due to barriers maintaining coverage associated with renewal processes and periodic eligibility checks,” Kaiser said.