The Shocking Secret About How Your Car Insurance Rate Gets Set

Most drivers probably know that if they get into an accident, their insurance rates are also likely to take a hit. But a new analysis by Consumer Reports finds that your car insurance premiums are increasingly based on factors such as your credit score that are unrelated to your driving record.
How well you drive may actually have little connection to how much you pay for insurance, the consumer group found.
In a two-year investigation, Consumer Reports analyzed more than 2 billion insurance price quotes obtained from more than 700 insurers across the country. It found that in many states a bad credit history will drive up your insurance premiums more than a drunk driving conviction.
“What we found is that behind the rate quotes is a pricing process that judges you less on driving habits and increasingly on socioeconomic factors,” the consumer organization reports. “These include your credit history, whether you use department-store or bank credit cards, and even your TV provider. Those measures are then used in confidential and often confounding scoring algorithms.”
Consumer Reports says it found that most car insurance companies use about 30 elements of the nearly 130 available in a credit report to construct their own secret score for policyholders, and that credit scores could have more of an impact on premiums than any other factor. Drivers with the best credit scores were charged up to $526 less than similar drivers with only “good” scores, depending on where they lived. Only three states — California, Hawaii and Massachusetts — prohibit insurers from factoring in credit scores when setting prices.
Drivers are legally required to carry car insurance, but the lack of pricing transparency makes it harder for them to make informed decisions about which policy to buy. “Because insurance companies are under no obligation to tell you what score they have cooked up for you, you have no idea whether you have a halo over your head or a bull’s-eye on your back for a price increase,” Consumer Reports says.
Industry advertising that promotes special discounts, such as for bundling home and car insurance, only muddles the purchasing process because those special deals don’t actually save people much money, Consumer Reports found.
The organization says it’s high time for truth in car insurance, and it’s asking consumers to sign a petition demanding that insurers -- and the state regulators who oversee them -- use price-setting practices that are tied to more meaningful factors, like driving records. It is also asking consumers to tweet the National Association of Insurance Commissioners, @NAIC_News, and tell them to “Price me by how I drive, not by who you think I am! #FixCarInsurance.”
For more information on state-by-state insurance premiums, or to sign the Consumer Reports petition, go to ConsumerReports.org/FixCarinsurance.
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times:
- Americans Are About to Get a Nice Fat Pay Raise
- How Millenials Could Damage the U.S. Economy
- The Pain the Job Numbers Don’t Show
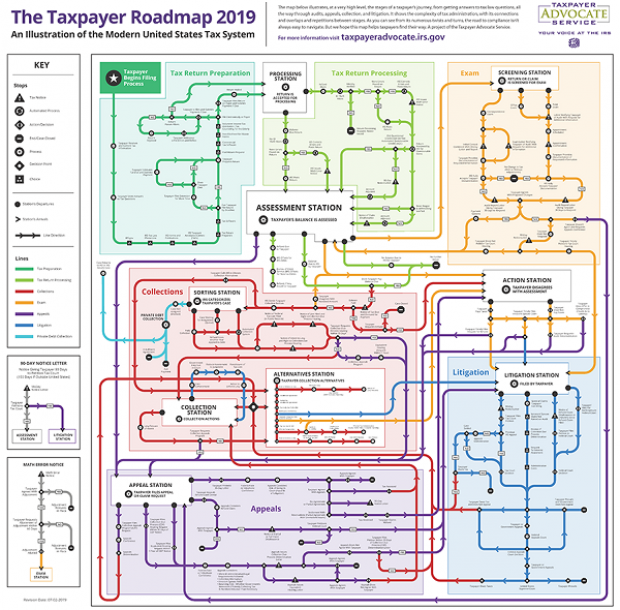
Map of the Day: Navigating the IRS

The Taxpayer Advocate Service – an independent organization within the IRS whose roughly 1,800 employees both assist taxpayers in resolving problems with the tax collection agency and recommend changes aimed at improving the system – released a “subway map” that shows the “the stages of a taxpayer’s journey.” The colorful diagram includes the steps a typical taxpayer takes to prepare and file their tax forms, as well as the many “stations” a tax return can pass through, including processing, audits, appeals and litigation. Not surprisingly, the map is quite complicated. Click here to review a larger version on the taxpayer advocate’s site.
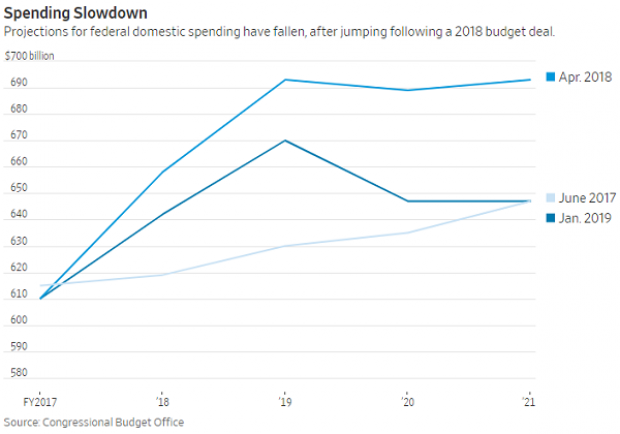
A Surprise Government Spending Slowdown

Economists expected federal spending to boost growth in 2019, but some of the fiscal stimulus provided by the 2018 budget deal has failed to show up this year, according to Kate Davidson of The Wall Street Journal.
Defense spending has come in as expected, but nondefense spending has lagged, and it’s unlikely to catch up to projections even if it accelerates in the coming months. Lower spending on disaster relief, the government shutdown earlier this year, and federal agencies spending less than they have been given by Congress all appear to be playing a role in the spending slowdown, Davidson said.
Number of the Day: $203,500

The Wall Street Journal’s Catherine Lucey reports that acting White House Chief of Staff Mick Mulvaney is making a bit more than his predecessors: “The latest annual report to Congress on White House personnel shows that President Trump’s third chief of staff is getting an annual salary of $203,500, compared with Reince Priebus and John Kelly, each of whom earned $179,700.” The difference is the result of Mulvaney still technically occupying the role of director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, where his salary level is set by law.
The White House told the Journal that if Mulvaney is made permanent chief of staff his salary would be adjusted to the current salary for an assistant to the president, $183,000.
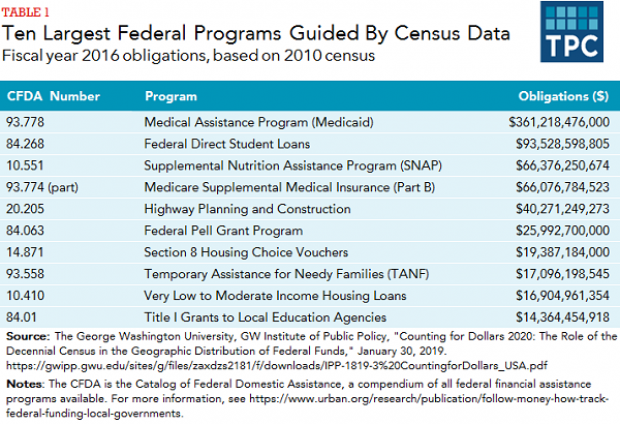
The Census Affects Nearly $1 Trillion in Spending

The 2020 census faces possible delay as the Supreme Court sorts out the legality of a controversial citizenship question added by the Trump administration. Tracy Gordon of the Tax Policy Center notes that in addition to the basic issue of political representation, the decennial population count affects roughly $900 billion in federal spending, ranging from Medicaid assistance funds to Section 8 housing vouchers. Here’s a look at the top 10 programs affected by the census:
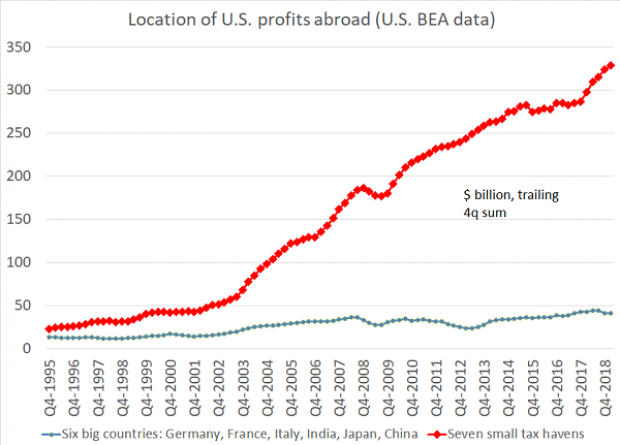
Chart of the Day: Offshore Profits Continue to Rise

Brad Setser, a former U.S. Treasury economist now with the Council on Foreign Relations, added another detail to his assessment of the foreign provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act: “A bit more evidence that Trump's tax reform didn't change incentives to offshore profits: the enormous profits that U.S. firms report in low tax jurisdictions continues to rise,” Setser wrote. “In fact, there was a bit of a jump up over the course of 2018.”