5 Cities with the Most Credit Card Debt
Why is the Lone Star State racking up so much debt? Its two largest cities—Dallas and Houston/Fort Worth make the list of the cities with the most credit card debt, and San Antonio comes in as No. 1.
The new study from CreditCards.com used credit report data from Experian to compare the average credit card debt in the 25 largest U.S. metro areas with each area’s median income. It assumed that 15 percent of a person's monthly income would be spent on paying down credit card debt.
The analysis claims it would take San Antonio residents with median incomes of $27,491 a full 16 months to pay off an average of $4,880, making monthly payments of $344 a month. By comparison, a resident of San Francisco making $42,613 a year would pay off $4,393 in credit card debt with nine monthly payments of $533 per month.
The cities with the highest credit card debt burdens were:
- San Antonio
- Dallas/Fort Worth
- Atlanta
- Miami/Fort Lauderdale
- Houston
Related: 5 Reasons to Pay Off Your Credit Card Debt Now
The metro areas with the highest debt don’t necessarily have the highest debt burdens when adjusted for income. For example, Washington, D.C. has the nation’s highest average credit card debt at $5,046, but since it also has the highest median income in the nation, its debt burden is lower. By applying 15 percent of their paychecks, residents can pay off that debt in 10 months.
The cities with the lowest credit card debt burdens were:
- New York City
- Minneapolis/St. Paul
- Washington, D.C.
- Boston
- San Francisco/Oakland/San Jose
Matt Schulz, senior industry analyst at CreditCards.com, points out that there isn’t much difference between the city with the highest credit card debt, Washington, D.C. ($5,046), and the city with the lowest credit card debt, the Riverside-San Bernardino area ($4,137), but there is a big difference in income. A higher income means that debts can be paid off more quickly. “It really is all about earnings,” Schulz says. “People are using their credit cards whether they live in the biggest city in the country or they live in the 25th biggest city in the country.”
While most folks won’t be able to increase their income that dramatically, there are still steps they can take to make sure they’re tackling their credit card debt in the most effective way possible.
Related: How to Defuse Exploding Consumer Credit Debt
His advice to consumers? “Absolutely, positively pay more than the minimum on your credit card balance every month.” And the next best thing? “If you can’t pay the full balance, then you have to pay off more than the minimum.”
Schulz also recommends calling the credit card issuer and asking if you can get better terms. “It’s certainly worth a call,” says Schulz. “We did a study last year that showed that 65 percent of people who asked for a lower interest rate got a lower APR.” The same study said that 86 percent of people who asked for a waiver of a late payment fee were successful in getting the charge removed.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- The Next Debt Crisis Could Be Much Worse than in 2013, GAO Warns
- The New Generation of ‘Genuinely Creepy’ Electronic Devices
- 9 Social Security Tips You Need to Know Right Now
The IRS Gives Hurricane Harvey Victims a Break
The tax agency announced Monday that “victims in parts of Texas have until Jan. 31, 2018, to file certain individual and business tax returns and make certain tax payments.”
Fitch Sends a Warning on US Credit Rating
One of the three major credit ratings agencies warned Wednesday that a failure to raise the debt ceiling could result in a lower credit rating for the U.S.
Fitch Ratings currently assigns a AAA rating to U.S. debt, the highest level possible. However, a failure to raise the debt ceiling "may not be compatible with 'AAA' status," according to the agency.
If the U.S. cannot sell more debt after bumping up against the debt ceiling, it may not be able to make all of its interest payments on time and in full. The federal government could begin running out of cash as soon as October.
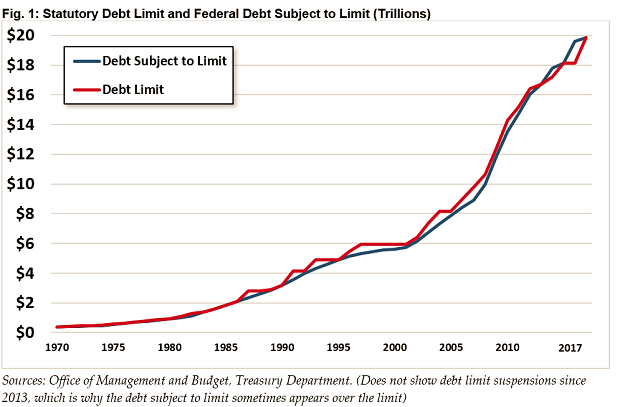
The debt ceiling is currently $19.9 trillion, and Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin has repeatedly urged Congress to raise the debt ceiling by September 29. A failure to do so could roil financial markets around the world, and ultimately increase the cost of servicing U.S. debt.
This is not the first time Congress has faced this problem. During an earlier debt ceiling showdown in 2011, Standard & Poor's reduced its rating on U.S. debt from its highest level to AA+. However, Fitch and Moody’s stuck with their top ratings.
Senators to Hold Hearings on a Bipartisan Fix for Health Care
Mark your calendars: Senate health committee Chairman Lamar Alexander (R-Tenn.) and Ranking Member Patty Murray (D-Wash.) announced today that they will hold bipartisan hearings on Sept. 6 and 7 focused on stabilizing premiums in the individual insurance market. The first hearing will be with state insurance commissioners; the second will be with governors.
In a statement, Alexander noted that 18 million Americans buy insurance on the individual market.
“My goal by the end of September is to give them peace of mind that they will be able to buy insurance at a reasonable price for the year 2018,” he said. “Unless Congress acts by September 27—when insurance companies must sign contracts with the federal government to sell insurance on the federal exchange in 2018— 9 million Americans in the individual market who receive no government help purchasing health insurance and whose premiums have already skyrocketed may see their premiums go up even more. Even those with subsidies in up to half our states may find themselves with zero options for buying health insurance on the Obamacare exchanges in 2018.”
McConnell: ‘Zero Chance’ the Debt Ceiling Will Be Breached
At an event in Kentucky to discuss tax reform, Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell and Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin insisted Monday that Congress will raise the debt ceiling by late next month, in time for the U.S. to avoid a default that could roil the global economy and markets.
Related: The Debt Ceiling — What It Is and Why We Should Care
The key quotes, per Roll Call:
McConnell: "There is zero chance — no chance — we won't raise the debt ceiling. No chance. America's not going to default. And we'll get the job done in conjunction with the secretary of the Treasury."
Mnuchin: “We’re going to get the debt ceiling passed. I think that everybody understands this is not a Republican issue, this is not a Democrat issue. We need to be able to pay our debts. This is about having a clean debt ceiling so that we can maintain the best credit, the reserve currency, and be focused on what we should be focusing on — so many other really important issues for the economy.”
Related: Here’s a Solution for the Annual Debt Ceiling Crisis — Get Rid of It
Mnuchin reiterated his “strong preference” for a “clean” increase to the debt limit — one without other policy proposals or spending cuts attached to it — but some House conservatives continue to press for such cuts.
Bonus McConnell quote on what tax breaks might be eliminated in tax reform: “I think there are only two things that the American people think are actually in the Constitution: The charitable deduction and the home mortgage interest deduction. So, if you’re worried about those two, you can breathe easy. For all the rest of you, there’s no point in doing tax reform unless we look at all of these preferences, and carried interest would be among them.”
Trump’s Travel and Family Size Squeeze Secret Service Budget
In an interview with USA Today, Secret Service Director Randolph "Tex" Alles said the agency is bumping up against federally mandated salary and overtime caps in executing its mission to protect the president and his family.
USA Today’s Kevin Johnson notes that 42 people in the Trump administration have Secret Service protection, including 18 of the president’s family members. Under President Obama, 31 people had such protection.
“The compensation crunch is so serious that the director has begun discussions with key lawmakers to raise the combined salary and overtime cap for agents, from $160,000 per year to $187,000 for at least the duration of Trump's first term,” Johnson reported.
Related: Which Former President Costs US the Most?
In a statement, Alles said the agency has the funding it needs for the rest of the fiscal year, which runs through Sept. 30, but estimated that 1,100 employees run into statutory pay caps as a result of overtime work during this calendar year.
“This issue is not one that can be attributed to the current Administration’s protection requirements alone, but rather has been an ongoing issue for nearly a decade due to an overall increase in operational tempo," Alles said in the statement.
Earlier: The Secret Service Won’t Get $60 Million More to Protect the Trumps
