5 Cities with the Most Credit Card Debt
Why is the Lone Star State racking up so much debt? Its two largest cities—Dallas and Houston/Fort Worth make the list of the cities with the most credit card debt, and San Antonio comes in as No. 1.
The new study from CreditCards.com used credit report data from Experian to compare the average credit card debt in the 25 largest U.S. metro areas with each area’s median income. It assumed that 15 percent of a person's monthly income would be spent on paying down credit card debt.
The analysis claims it would take San Antonio residents with median incomes of $27,491 a full 16 months to pay off an average of $4,880, making monthly payments of $344 a month. By comparison, a resident of San Francisco making $42,613 a year would pay off $4,393 in credit card debt with nine monthly payments of $533 per month.
The cities with the highest credit card debt burdens were:
- San Antonio
- Dallas/Fort Worth
- Atlanta
- Miami/Fort Lauderdale
- Houston
Related: 5 Reasons to Pay Off Your Credit Card Debt Now
The metro areas with the highest debt don’t necessarily have the highest debt burdens when adjusted for income. For example, Washington, D.C. has the nation’s highest average credit card debt at $5,046, but since it also has the highest median income in the nation, its debt burden is lower. By applying 15 percent of their paychecks, residents can pay off that debt in 10 months.
The cities with the lowest credit card debt burdens were:
- New York City
- Minneapolis/St. Paul
- Washington, D.C.
- Boston
- San Francisco/Oakland/San Jose
Matt Schulz, senior industry analyst at CreditCards.com, points out that there isn’t much difference between the city with the highest credit card debt, Washington, D.C. ($5,046), and the city with the lowest credit card debt, the Riverside-San Bernardino area ($4,137), but there is a big difference in income. A higher income means that debts can be paid off more quickly. “It really is all about earnings,” Schulz says. “People are using their credit cards whether they live in the biggest city in the country or they live in the 25th biggest city in the country.”
While most folks won’t be able to increase their income that dramatically, there are still steps they can take to make sure they’re tackling their credit card debt in the most effective way possible.
Related: How to Defuse Exploding Consumer Credit Debt
His advice to consumers? “Absolutely, positively pay more than the minimum on your credit card balance every month.” And the next best thing? “If you can’t pay the full balance, then you have to pay off more than the minimum.”
Schulz also recommends calling the credit card issuer and asking if you can get better terms. “It’s certainly worth a call,” says Schulz. “We did a study last year that showed that 65 percent of people who asked for a lower interest rate got a lower APR.” The same study said that 86 percent of people who asked for a waiver of a late payment fee were successful in getting the charge removed.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- The Next Debt Crisis Could Be Much Worse than in 2013, GAO Warns
- The New Generation of ‘Genuinely Creepy’ Electronic Devices
- 9 Social Security Tips You Need to Know Right Now
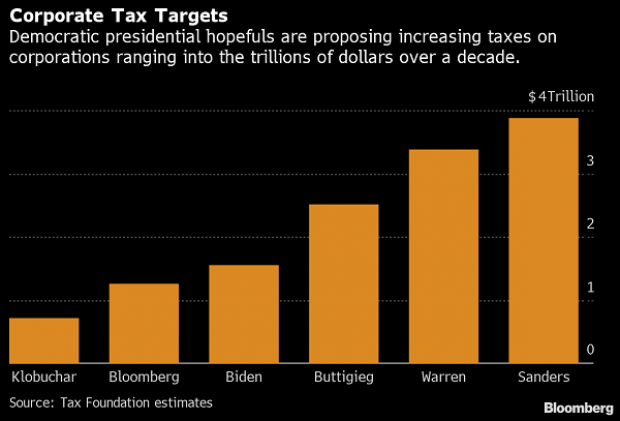
Chart of the Day: Boosting Corporate Tax Revenues

The leading candidates for the Democratic presidential nomination have all proposed increasing taxes on corporations, including raising income tax rates to levels ranging from 25% to 35%, up from the current 21% imposed by the Republican tax cuts in 2017. With Bernie Sanders leading the way at $3.9 trillion, here’s how much revenue the higher proposed corporate taxes, along with additional proposed surtaxes and reduced tax breaks, would generate over a decade, according to calculations by the right-leaning Tax Foundation, highlighted Wednesday by Bloomberg News.
Chart of the Day: Discretionary Spending Droops
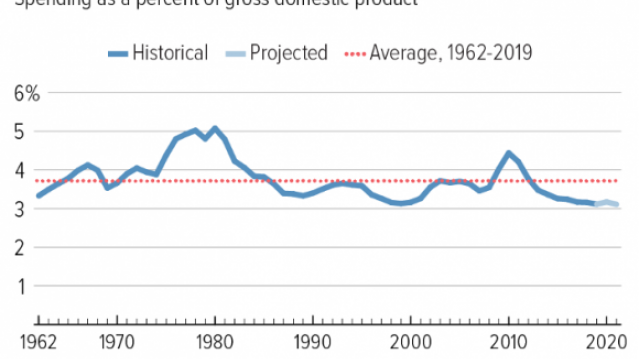
The federal government’s total non-defense discretionary spending – which covers everything from education and national parks to veterans’ medical care and low-income housing assistance – equals 3.2% of GDP in 2020, near historic lows going back to 1962, according to an analysis this week from the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Chart of the Week: Trump Adds $4.7 Trillion in Debt
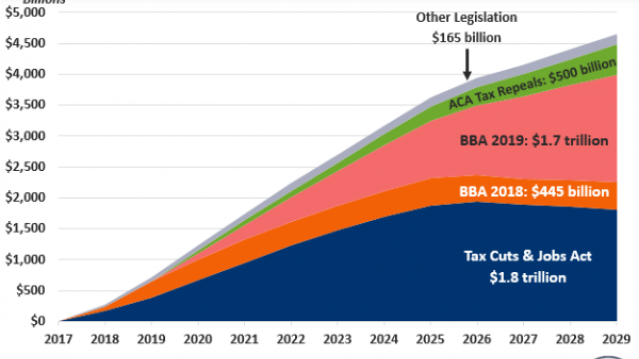
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget estimated this week that President Trump has now signed legislation that will add a total of $4.7 trillion to the national debt between 2017 and 2029. Tax cuts and spending increases account for similar portions of the projected increase, though if the individual tax cuts in the 2017 Republican overhaul are extended beyond their current expiration date at the end of 2025, they would add another $1 trillion in debt through 2029.
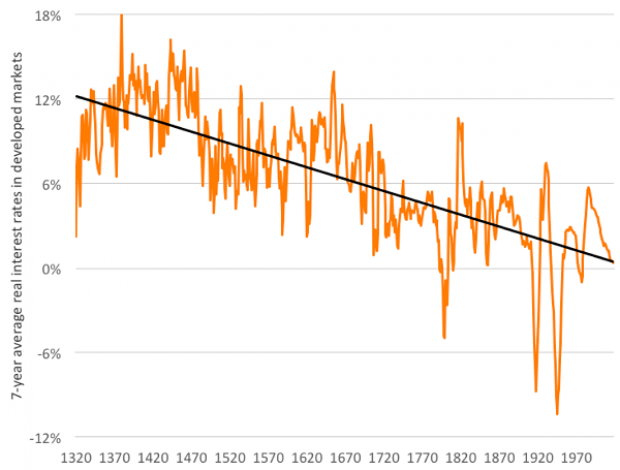
Chart of the Day: The Long Decline in Interest Rates
Are interest rates destined to move higher, increasing the cost of private and public debt? While many experts believe that higher rates are all but inevitable, historian Paul Schmelzing argues that today’s low-interest environment is consistent with a long-term trend stretching back 600 years.
The chart “shows a clear historical downtrend, with rates falling about 1% every 60 years to near zero today,” says Bloomberg’s Aaron Brown. “Rates do tend to revert to a mean, but that mean seems to be declining.”
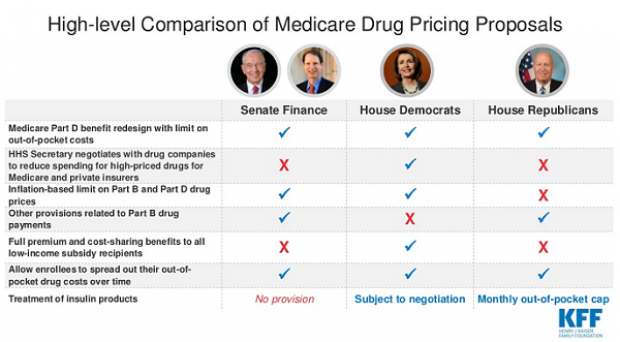
Chart of the Day: Drug Price Plans Compared
Lawmakers are considering three separate bills that are intended to reduce the cost of prescription drugs. Here’s an overview of the proposals, from a series of charts produced by the Kaiser Family Foundation this week. An interesting detail highlighted in another chart: 88% of voters – including 92% of Democrats and 85% of Republicans – want to give the government the power to negotiate prices with drug companies.