Thync Before You Act – A New Wearable Device Made for 'The Donald'

If you thought people looked foolish wearing Google Glass, wait until you see one of your coworkers sticking a white piece of plastic on her forehead, hooked around her ear. I learned about Thync, a $300 electric gizmo, reading Geoffrey Fowler’s Wall Street Journal column Tuesday.
Fowler tested it, so I don’t have to, but I just know I’ll be seeing this piece of wearable tech around town among the gadgerati I sometimes hang out with. Thync’s unique selling proposition is vibes, uncommonly known as transdermal electrical neuromodulation. Translation—it’s a low-grade form of shock therapy. The company says they’ve tested the device over years of research with their neuroscientists and engineers to give us Calm vibes or Energy vibes.

You’ll have to go to Fowler’s story to view a graphic of how this dildo for the brain actually functions, but Folwer describes the Energy vibe this way: “The sensation is like drinking an espresso, accompanied by a tingle of prickly heat behind the ear.” He compares the hour-long Calm vibe to having a glass of wine.
Like everything else related to wearable tech and the Internet of Things, the company is well funded by Silicon Valley venture capital firms, which are apparently looking for the next Fitbit. And why not? Brain fitness. I know a few people who could benefit from Thync if it works as promised.
Let’s start by getting the company to give one to Donald Trump, set it permanently on the Calm setting, and turn up the juice.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- Six Amazing Features Hidden in Your Smartphone
- Facebook Must Hand Over NY Users' Info to Prosecutors
- The Incredible Disappearing American-Made Car
Stat of the Day: 0.2%

The New York Times’ Jim Tankersley tweets: “In order to raise enough revenue to start paying down the debt, Trump would need tariffs to be ~4% of GDP. They're currently 0.2%.”
Read Tankersley’s full breakdown of why tariffs won’t come close to eliminating the deficit or paying down the national debt here.
Number of the Day: 44%

The “short-term” health plans the Trump administration is promoting as low-cost alternatives to Obamacare aren’t bound by the Affordable Care Act’s requirement to spend a substantial majority of their premium revenues on medical care. UnitedHealth is the largest seller of short-term plans, according to Axios, which provided this interesting detail on just how profitable this type of insurance can be: “United’s short-term plans paid out 44% of their premium revenues last year for medical care. ACA plans have to pay out at least 80%.”
Number of the Day: 4,229

The Washington Post’s Fact Checkers on Wednesday updated their database of false and misleading claims made by President Trump: “As of day 558, he’s made 4,229 Trumpian claims — an increase of 978 in just two months.”
The tally, which works out to an average of almost 7.6 false or misleading claims a day, includes 432 problematics statements on trade and 336 claims on taxes. “Eighty-eight times, he has made the false assertion that he passed the biggest tax cut in U.S. history,” the Post says.
Number of the Day: $3 Billion

A new analysis by the Department of Health and Human Services finds that Medicare’s prescription drug program could have saved almost $3 billion in 2016 if pharmacies dispensed generic drugs instead of their brand-name counterparts, Axios reports. “But the savings total is inflated a bit, which HHS admits, because it doesn’t include rebates that brand-name drug makers give to [pharmacy benefit managers] and health plans — and PBMs are known to play games with generic drugs to juice their profits.”
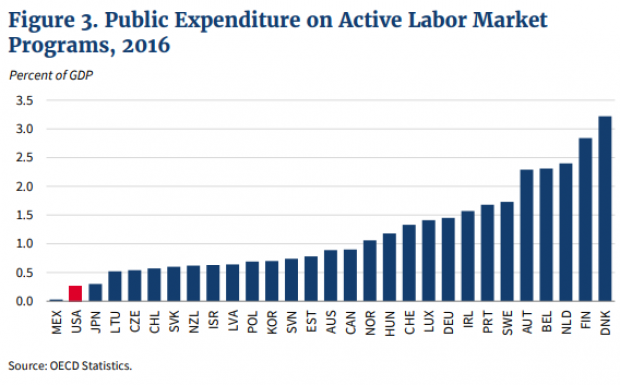
Chart of the Day: Public Spending on Job Programs

President Trump announced on Thursday the creation of a National Council for the American Worker, charged with developing “a national strategy for training and retraining workers for high-demand industries,” his daughter Ivanka wrote in The Wall Street Journal. A report from the president’s National Council on Economic Advisers earlier this week made it clear that the U.S. currently spends less public money on job programs than many other developed countries.