Here’s the Scoop: Fun Facts for National Ice Cream Day

When President Ronald Reagan in 1984 designated the month of July as National Ice Cream Month and declared the third Sunday of July as National Ice Cream Day, he probably never could have foreseen a time when flavors of the treat included Pork Rind, Strawberry Durian or Squid.
Ice cream shops around the country will be celebrating their special day again this Sunday, July 19. Carvel stores will be offering a buy-one-get-one-free deal on any size or flavor of soft-serve cones. Friendly’s is celebrating its 80th birthday this weekend, with participating stores also offering buy-one-get-one-free deals. Baskin-Robbins is offering a free upgrade to waffle cones with double scoops during the entire month of July. It also will offer 31 percent off all its ice cream sundaes on Friday, July 31.
Related: Born in the USA: 24 Iconic American Foods
Those chains offer a wide variety of flavors, but probably nothing quite as exotic as the OddFellows Ice Cream Co. in New York City, known for formulations loaded with unusual ingredients: Edamame, Chorizo Caramel Swirl, Cornbread and Maple Bacon Pecan. OddFellows co-owner Mohan Kumar says National Ice Cream Day will be just a regular Sunday for him and his stores: “It’s a beautiful day for ice cream every day.”
As you consider indulging in a frozen snack, here are some fun facts to fuel our red hot passion for ice cream:
Who Screams for Ice Cream: California, Indiana, Pennsylvania, Texas and New York are the states that consume the most ice cream. California also produces the most ice cream—over 142,000 gallons every year. About 10.3 percent of all the milk produced by U.S. dairy farmers is used to make ice cream. The five most popular brands in the U.S. are private labels, followed by Blue Bell, Haagen-Dazs, Breyers and Ben & Jerry’s. According to the International Dairy Foods Association, vanilla is America’s favorite flavor of ice cream, followed by chocolate. And how’s this for being ice cream crazy? Ben & Jerry’s employees get three free pints a day. They also get a free gym membership.
Hard Facts About Soft Serve: Despite many headlines to the contrary, it does not look like former British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher invented soft-serve ice cream before she became known as the Iron Lady. The honor instead goes to Tom Carvel of Carvel ice cream or Dairy Queen co-founder J. F. McCullough. In Carvel’s case, his ice cream truck got a flat tire in Hartsdale, New York, in 1934. As the ice cream started to melt, he noticed its soft, creamy consistency and began selling it right from the truck. Two years later, he opened his first Carvel shop at the site where the truck first broke down.
Related: The 9 Most Expensive Junk Foods
Why We’re All Coneheads: Italo Marchiony, an Italian immigrant, was granted a patent for waffle-like ice cream cups in New York City in December 1903. But he may not be the father of the cones we enjoy today. As the story goes, Arnold Fornachou, an ice cream vendor at the 1904 World’s Fair in St. Louis, ran out of dishes. His neighbor, a Syrian man, was selling crisp, Middle Eastern pastries called Zalabias. When rolled up, the waffle-like Zalabias made a perfect cone to hold the ice cream. The International Association of Ice Cream Manufacturers and the International Dairy Foods Association credit Ernest A. Hamwi, the pastry maker, with creating the cone, but others have also claimed credit — including Abe Doumar, another Syrian immigrant at the 1904 fair who would go on to produce the first machine to mass-produce ice cream waffle cones.
Facebook Is Testing a Solar-Powered Internet-Beaming Drone

Imagine looking up at the sky and seeing a 900 lb. drone the size of Boeing 737 moving in slow circles 11 miles above you. As part of Facebook’s plan to provide Internet access to the 4 billion people who currently lack it, that could soon be the reality for the 10 percent of Earth’s population that lives far from cell towers or fiber optic lines.
Researchers at Facebook’s Connectivity Lab, a division of Facebook’s Internet.org, announced yesterday that the first such drone has been completed as a step toward building a larger fleet. The craft hasn’t been flown yet, but Facebook has been testing versions one-tenth the size over the U.K. and plans on beginning flight tests of the full-size craft before the end of this year.
Related: 12 Weird Uses for Drones
The drone, termed Aquila (Latin for “Eagle), is a solar-powered V-shaped carbon fiber craft that will carry equipment such as solar panels and communications gear that can beam down wireless Internet connectivity. Lacking wheels or the ability to climb, the drone will be launched using helium balloons and will be able to fly for 90 days at a time.
One of the biggest breakthroughs in the project has been the team developing a way to increase the data capacity of the lasers involved. The new system allows a ground-based laser to transmit information to a dome on the underside of the plane at 10 GB per second, about 10 times faster than previously thought possible.
Facebook’s mission isn’t without controversy. Worldwide, critics have been questioning many of Internet.org’s practices on privacy, fairness and security grounds. Those opponents fear that users of Internet.org might be monitored through state-run telecoms, in some cases allowing countries to spy on and repress their citizens. In addition, first-time users of the Internet might confuse Facebook for the entire Internet and only receive news and information from the one site.
The flack Internet.org is receiving isn’t the only problem Facebook has to deal with. Rival Google also has a project in the works to bring wireless Internet to rural communities. Their program, called “Project Loon,” involves high-altitude helium balloons that have transmitters attached to them. Although the project hasn’t been launched yet, it’s in more advanced stages than Aquila.
Watch the video from Facebook’s Connectivity Lab:
This Is the Most Annoying Thing About Customer Service

The number of Americans fed up with lousy customer service is decreasing but there are still some practices that irritate nearly everyone, according to a newly published report in Consumer Reports’ September issue.
There was a tie for the top customer service complaint. Seventy-five per percent of shoppers surveyed were annoyed by the inability to get a live person on the phone and by dealing with a representative who was rude or condescending.
Seventy-four percent of consumers said they were highly annoyed at being disconnected from a customer service rep, and 71 percent were dissatisfied that they’d been disconnected and then unable to reach the same representative again.
“Many companies today are simply awful at resolving customer protections, despite investments in whiz-bang technologies and considerable advertising about their customer focus,” Scott Broetzman, president of Customer Care Measurement & Consulting, told the magazine.
In a separate report released this week, 24/7 Wall Street found that Amazon.com is the best big company for customer service, followed by Chick-fil-A and Apple. The companies in the publication’s “Customer Service Hall of Shame” include Bank of America, DirectTV and Comcast.
In order to get the best possible customer service, Consumer Reports recommends using the phone, rather than email; showing—and asking for—empathy; and escalating when necessary.
The magazine also suggests putting technology to work. The website Dial a Human can help find the best customer service number for a company, and the service Lucy Phone lets you enter a company’s name and number and then calls you when a rep becomes available so you don’t have to wait on hold.
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times:
- The Next Debt Crisis Could Be Much Worse than in 2013, GAO Warns
- The New Generation of ‘Genuinely Creepy’ Electronic Devices
- Who Are These People Giving Money to Donald Trump?
The Weakest Economic Recovery Since World War II Putters Along

New GDP data released today shows an economy that continues to grow, though at a disappointingly moderate pace.
The good news is that GDP growth picked up after the weak, snow-encrusted first quarter of 2015, when the economy eked out a 0.6 percent growth rate. The bad news is that growth was expected to hit a 2.5 percent rate or better in the second quarter, but initial estimates arriving today pegged that rate at 2.3 percent. Over the first six months of the year, the economy has expanded at an annual rate of 1.5 percent.
The U.S. recession officially ended in the second quarter of 2009. Since then, growth has been relatively steady but lackluster. Compared to other recoveries since the end of World War II, the current recovery is notably weak – without question the weakest of the bunch. The average annual growth rate from 2011 through 2014 was 2.0 percent, based on updated figured released today.
Economists have argued about the causes — a glut of capital, excessive regulation, the domination of finance, low wages driving weak demand — but the simple fact remains: This is a feeble recovery.
This graphic we produced on the Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis’s website tells the story – look for the bright red line:

Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- The Kids Aren't Alright: More Millenials Are Living with Their Parents
- How Millenials Could Damage the U.S. Economy
- The Pain the Job Numbers Don’t Show
The Shocking Secret About How Your Car Insurance Rate Gets Set

Most drivers probably know that if they get into an accident, their insurance rates are also likely to take a hit. But a new analysis by Consumer Reports finds that your car insurance premiums are increasingly based on factors such as your credit score that are unrelated to your driving record.
How well you drive may actually have little connection to how much you pay for insurance, the consumer group found.
In a two-year investigation, Consumer Reports analyzed more than 2 billion insurance price quotes obtained from more than 700 insurers across the country. It found that in many states a bad credit history will drive up your insurance premiums more than a drunk driving conviction.
“What we found is that behind the rate quotes is a pricing process that judges you less on driving habits and increasingly on socioeconomic factors,” the consumer organization reports. “These include your credit history, whether you use department-store or bank credit cards, and even your TV provider. Those measures are then used in confidential and often confounding scoring algorithms.”
Consumer Reports says it found that most car insurance companies use about 30 elements of the nearly 130 available in a credit report to construct their own secret score for policyholders, and that credit scores could have more of an impact on premiums than any other factor. Drivers with the best credit scores were charged up to $526 less than similar drivers with only “good” scores, depending on where they lived. Only three states — California, Hawaii and Massachusetts — prohibit insurers from factoring in credit scores when setting prices.
Drivers are legally required to carry car insurance, but the lack of pricing transparency makes it harder for them to make informed decisions about which policy to buy. “Because insurance companies are under no obligation to tell you what score they have cooked up for you, you have no idea whether you have a halo over your head or a bull’s-eye on your back for a price increase,” Consumer Reports says.
Industry advertising that promotes special discounts, such as for bundling home and car insurance, only muddles the purchasing process because those special deals don’t actually save people much money, Consumer Reports found.
The organization says it’s high time for truth in car insurance, and it’s asking consumers to sign a petition demanding that insurers -- and the state regulators who oversee them -- use price-setting practices that are tied to more meaningful factors, like driving records. It is also asking consumers to tweet the National Association of Insurance Commissioners, @NAIC_News, and tell them to “Price me by how I drive, not by who you think I am! #FixCarInsurance.”
For more information on state-by-state insurance premiums, or to sign the Consumer Reports petition, go to ConsumerReports.org/FixCarinsurance.
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times:
- Americans Are About to Get a Nice Fat Pay Raise
- How Millenials Could Damage the U.S. Economy
- The Pain the Job Numbers Don’t Show
The Kids Aren’t Alright: More Millennials Are Living with Their Parents

Pity the millennial, poster child of the Great Recession. A popular meme portrays the typical millennial as a basement-dwelling economic loser, forever condemned to live in the nether regions of his parent’s house. Unfortunately, that meme is not without basis. The recession seem to have hit millennials particularly hard, making it even more difficult for young people to find good jobs and to establish their own households.
In some respects, things are looking up for millennials. The U.S. job market is strengthening, making it easier to find work, and wages are starting to creep higher. The unemployment rate for young adults (ages 18 to 34, excluding full-time college students) has been heading lower since peaking near 12 percent in 2010; the latest unemployment reading for millennials is 7.7 percent.
However, there is one notable sticking point, and it echoes that basement-dwelling meme. Even though household formation rates have rebounded overall, millennials are still not moving out and establishing their own households like they used to. In fact, more millennials are living with parents or relatives than before the recession, according to new research from Pew.
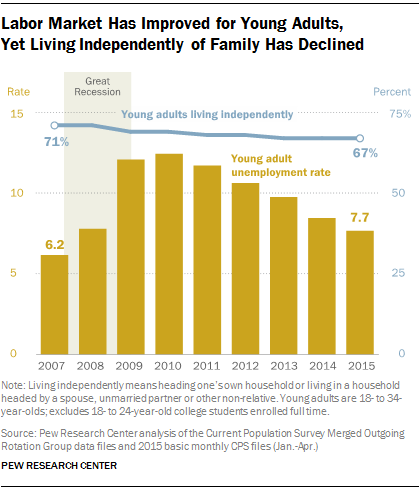
In 2007, before the recession hit, 71 percent of millennials were living independently. In 2015, that number has fallen to 67 percent, with no sign of bottoming.
On the flip side, 22 percent of young adults were living in their parents’ homes in 2007. That number has risen to 26 percent this year.
The Pew report doesn’t look at why millennials are sticking so close to home. However, it does suggest that the relatively simple economic argument about the lack of good jobs no longer tells the whole story. Since the economy is recovering, however unevenly, there are likely other factors in play. One could be cultural: More young people simply enjoy living at home and are in no hurry to move out. Perhaps the U.S. is becoming more like Italy, where adult children often live at home until they marry.
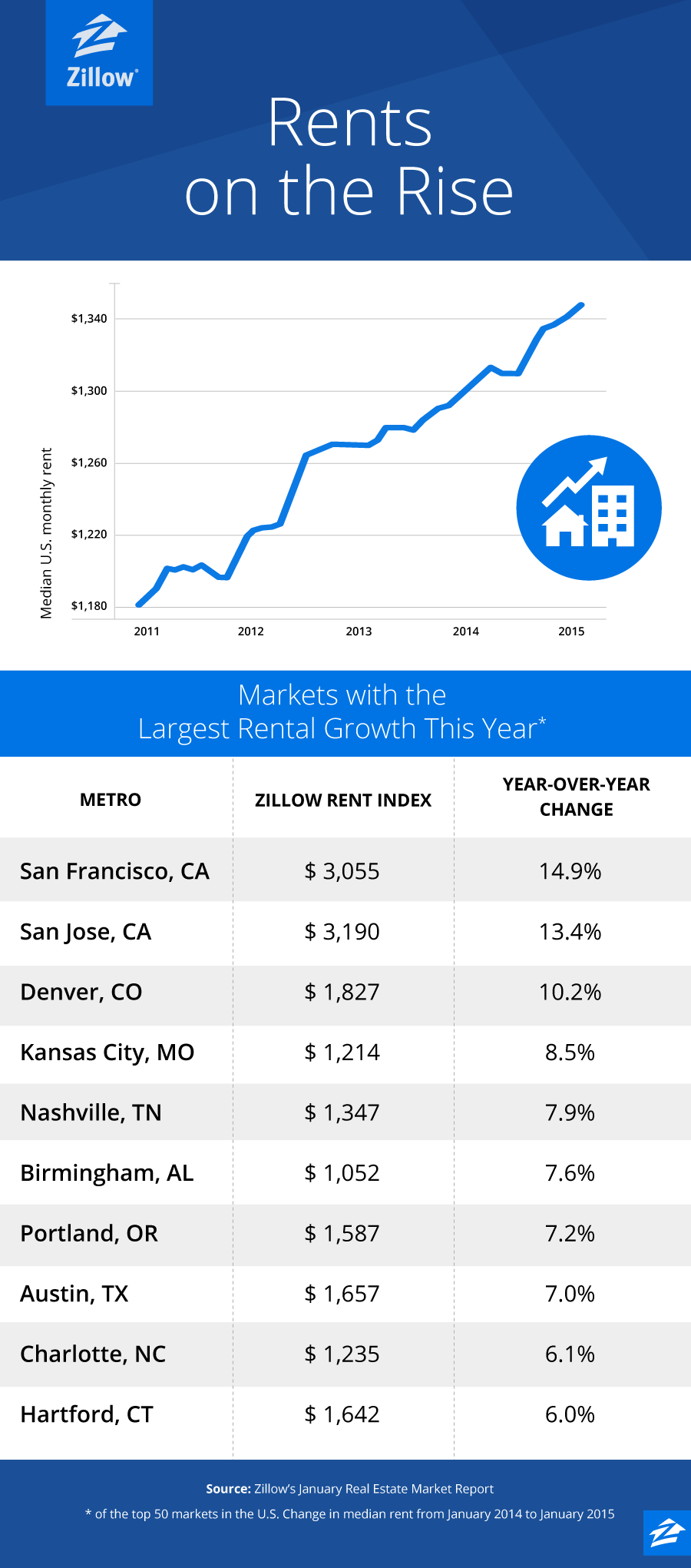
That’s not to say that money plays no role in the trend, though. One big economic factor not addressed in the Pew report is pretty basic: rising rents. This graphic from Zillow makes it clear that rents have been soaring all over the country. More than $3,000 for a one bedroom in San Francisco? With those kind of numbers, living at home makes all the sense in the world.