Tiny Bubbles, Big Business: How Seltzer Became the Hot New Drink

Struggling to decide between healthy but boring water and sweet, sugary soda, Americans are increasingly turning to fizzy water to quench their thirst.
Although soda remains the leader in the soft drink category, soda consumption has fallen for the 10th year in a row, to the lowest level since 1986, according to The Wall Street Journal. Americans have been dropping sugary soda for years due to health concerns, but lately even diet soda has been losing popularity over worries about artificial sweeteners.
Sales of fizzy water — the category includes such well-known brands as Perrier and San Pellegrino — have grown to about $1.5 billion a year, more than doubling since 2010, according to data from industry research firm Euromonitor quoted in The Washington Post.
Related: How Coke Beat Pepsi in the New Cola Ad War
One of the top new brands is National Beverage’s LaCroix Sparkling Water, whose dozen flavors of bubbly H20 seem to be aimed at millennials in particular. The brand’s bright, colorful cans convey an alternative vibe, and the drink’s Instagram is loaded with attractive young people hoisting a can at pools, beaches and other relaxing places.
National Beverage credited sparkling water as the main factor that grew the company’s stock 75 percent over the last five years. Sales of the LaCroix brand alone have grown to $175 million, almost tripling since 2009.
Another rapidly growing brand, Sparkling Ice, owned by Talking Rain Beverage Company, saw sales boom to more than $384 million in 2014 from $2.7 million in 2009.
Gary Hemphill, managing director and COO of research at Beverage Marketing, sees the sales of seltzer and sparkling water only increasing as consumer demand for healthier refreshments grows.
Deficit Hits $738.6 Billion in First 8 Months of Fiscal Year

The U.S. budget deficit grew to $738.6 billion in the first eight months of the current fiscal year – an increase of $206 billion, or 38.8%, over the deficit recorded during the same period a year earlier. Bloomberg’s Sarah McGregor notes that the big increase occurred despite a jump in tariff revenues, which have nearly doubled to $44.9 billion so far this fiscal year. But that increase, which contributed to an overall increase in revenues of 2.3%, was not enough to make up for the reduced revenues from the Republican tax cuts and a 9.3% increase in government spending.
Tweet of the Day: Revenues or Spending?

Rep. Kevin Brady (R-TX), ranking member of the House Ways and Means Committee and one of the authors of the 2017 Republican tax overhaul, told The Washington Post’s Heather Long Tuesday that the budget deficit is driven by excess spending, not a shortfall in revenues in the wake of the tax cuts. The Wall Street Journal’s Kate Davidson provided some inconvenient facts for Brady’s claim in a tweet, pointing out that government revenues as a share of GDP have fallen significantly since 2015, while spending has remained more or less constant.
Chart of the Day: The Decline in IRS Audits

Reviewing the recent annual report on tax statistics from the IRS, Robert Weinberger of the Tax Policy Center says it “tells a story of shrinking staff, fewer audits, and less customer service.” The agency had 22% fewer personnel in 2018 than it did in 2010, and its enforcement budget has fallen by nearly $1 billion, Weinberger writes. One obvious effect of the budget cuts has been a sharp reduction in the number of audits the agency has performed annually, which you can see in the chart below.
Number of the Day: $102 Million

President Trump’s golf playing has cost taxpayers $102 million in extra travel and security expenses, according to an analysis by the left-leaning HuffPost news site.
“The $102 million total to date spent on Trump’s presidential golfing represents 255 times the annual presidential salary he volunteered not to take. It is more than three times the cost of special counsel Robert Mueller’s investigation that Trump continually complains about. It would fund for six years the Special Olympics program that Trump’s proposed budget had originally cut to save money,” HuffPost’s S.V. Date writes.
Date says the White House did not respond to HuffPost’s requests for comment.
Americans See Tax-Paying as a Duty

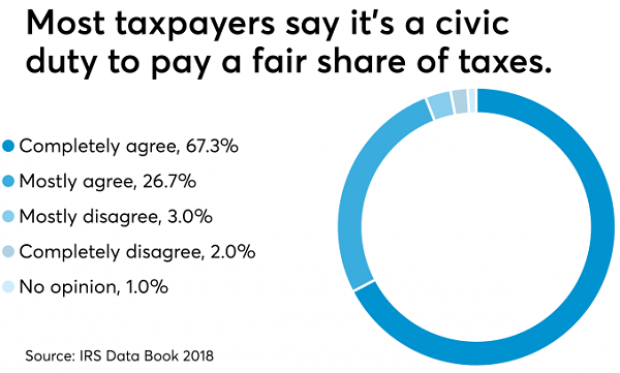
The IRS may not be conducting audits like it used to, but according to the agency’s Data Book for 2018, most Americans still believe it’s not acceptable to cheat on your taxes. About 67% of respondents to an IRS opinion survey “completely agree” that it’s a civic duty to pay “a fair share of taxes,” and another 26% “mostly agree,” bringing the total in agreement to over 90%. Accounting Today says that attitude has been pretty consistent over the last decade.