Tiny Bubbles, Big Business: How Seltzer Became the Hot New Drink

Struggling to decide between healthy but boring water and sweet, sugary soda, Americans are increasingly turning to fizzy water to quench their thirst.
Although soda remains the leader in the soft drink category, soda consumption has fallen for the 10th year in a row, to the lowest level since 1986, according to The Wall Street Journal. Americans have been dropping sugary soda for years due to health concerns, but lately even diet soda has been losing popularity over worries about artificial sweeteners.
Sales of fizzy water — the category includes such well-known brands as Perrier and San Pellegrino — have grown to about $1.5 billion a year, more than doubling since 2010, according to data from industry research firm Euromonitor quoted in The Washington Post.
Related: How Coke Beat Pepsi in the New Cola Ad War
One of the top new brands is National Beverage’s LaCroix Sparkling Water, whose dozen flavors of bubbly H20 seem to be aimed at millennials in particular. The brand’s bright, colorful cans convey an alternative vibe, and the drink’s Instagram is loaded with attractive young people hoisting a can at pools, beaches and other relaxing places.
National Beverage credited sparkling water as the main factor that grew the company’s stock 75 percent over the last five years. Sales of the LaCroix brand alone have grown to $175 million, almost tripling since 2009.
Another rapidly growing brand, Sparkling Ice, owned by Talking Rain Beverage Company, saw sales boom to more than $384 million in 2014 from $2.7 million in 2009.
Gary Hemphill, managing director and COO of research at Beverage Marketing, sees the sales of seltzer and sparkling water only increasing as consumer demand for healthier refreshments grows.
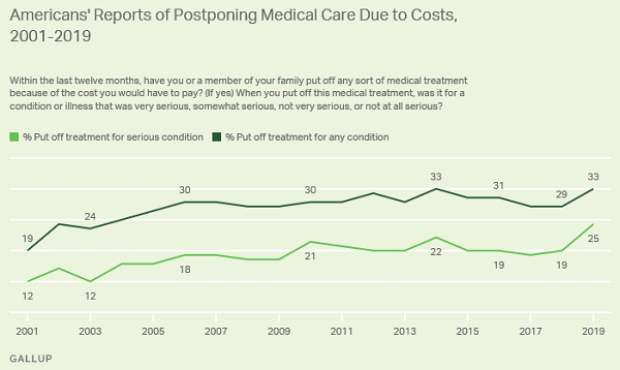
Increasing Number of Americans Delay Medical Care Due to Cost: Gallup

From Gallup: “A record 25% of Americans say they or a family member put off treatment for a serious medical condition in the past year because of the cost, up from 19% a year ago and the highest in Gallup's trend. Another 8% said they or a family member put off treatment for a less serious condition, bringing the total percentage of households delaying care due to costs to 33%, tying the high from 2014.”
Number of the Day: $213 Million

That’s how much the private debt collection program at the IRS collected in the 2019 fiscal year. In the black for the second year in a row, the program cleared nearly $148 million after commissions and administrative costs.
The controversial program, which empowers private firms to go after delinquent taxpayers, began in 2004 and ran for five years before the IRS ended it following a review. It was restarted in 2015 and ran at a loss for the next two years.
Senate Finance Chairman Chuck Grassley (R-IA), who played a central role in establishing the program, said Monday that the net proceeds are currently being used to hire 200 special compliance personnel at the IRS.
US Deficit Up 12% to $342 Billion for First Two Months of Fiscal 2020: CBO

The federal budget deficit for October and November was $342 billion, up $36 billion or 12% from the same period last year, the Congressional Budget Office estimated on Monday. Revenues were up 3% while outlays rose by 6%, CBO said.
Hospitals Sue to Protect Secret Prices

As expected, groups representing hospitals sued the Trump administration Wednesday to stop a new regulation would require them to make public the prices for services they negotiate with insurers. Claiming the rule “is unlawful, several times over,” the industry groups, which include the American Hospital Association, say the rule violates their First Amendment rights, among other issues.
"The burden of compliance with the rule is enormous, and way out of line with any projected benefits associated with the rule," the suit says. In response, a spokesperson for the Department of Health and Human Services said that hospitals “should be ashamed that they aren’t willing to provide American patients the cost of a service before they purchase it.”
See the lawsuit here, or read more at The New York Times.
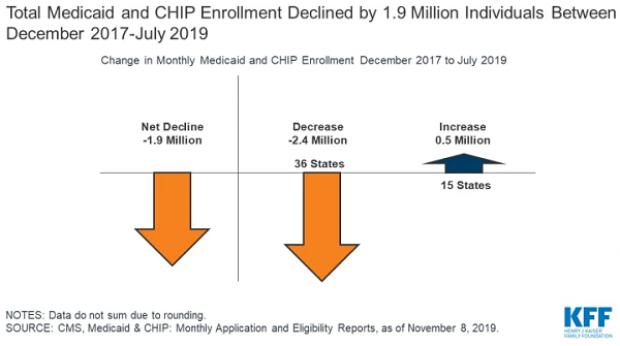
A Decline in Medicaid and CHIP Enrollment
Between December 2017 and July 2019, enrollment in Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) fell by 1.9 million, or 2.6%. The Kaiser Family Foundation provided an analysis of that drop Monday, saying that while some of it was likely caused by enrollees finding jobs that offer private insurance, a significant portion is related to enrollees losing health insurance of any kind. “Experiences in some states suggest that some eligible people may be losing coverage due to barriers maintaining coverage associated with renewal processes and periodic eligibility checks,” Kaiser said.