Why You Might Want to Cancel That Restaurant Reservation

The cost of dining out rose 3 percent in May year-over-year, while the amount paid to eat at home inched up just 0.6 percent. The growing disparity in prices could prompt consumers to abandon restaurants for home-cooked meals, according to a report today by Bloomberg.
“Eating in hasn’t been this attractive compared to dining out since 2010,” Bloomberg reports. That’s good news for consumers worried about their budgets, but could be a problem for restaurants’ bottom lines.
So far, consumers aren’t making the shift. This spring, spending at restaurants and bars totaled more than sales at grocery stores for the first time.
Related: The 11 Worst Fast Food Restaurants in America
Part of the reason consumers are sticking with restaurants could be that wages are starting to slowly increase, so consumers have a little more money to spend on meals.
They may also be dining out because it’s often an easier option. Shopping and preparing meals takes time – time that people simply don’t have these days. A quarter of employees say that they are working after the standard work day has ended, and about 40 percent work at least one weekend a month, according to Staples Advantage. That leaves little time for food prep.
Supermarkets have responded to the time-pressed consumer by increasingly offering prepared meals that require little more than reheating at home. The prices for such meals tend to be higher than the cost of their ingredients but less than the price of eating out or ordering in.
Tax Refunds Rebound

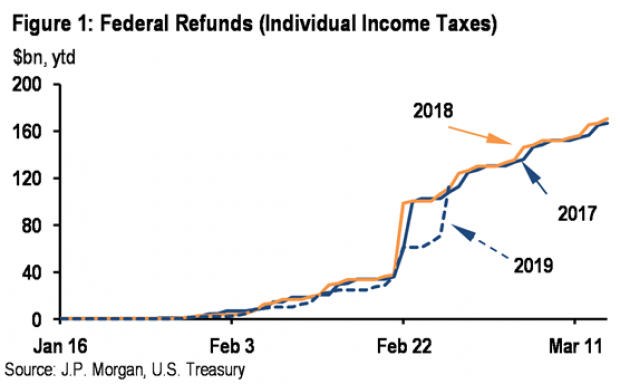
Smaller refunds in the first few weeks of the current tax season were shaping up to be a political problem for Republicans, but new data from the IRS shows that the value of refund checks has snapped back and is now running 1.3 percent higher than last year. The average refund through February 23 last year was $3,103, while the average refund through February 22 of 2019 was $3,143 – a difference of $40. The chart below from J.P. Morgan shows how refunds performed over the last 3 years.
Number of the Day: $22 Trillion

The total national debt surpassed $22 trillion on Monday. Total public debt outstanding reached $22,012,840,891,685.32, to be exact. That figure is up by more than $1.3 trillion over the past 12 months and by more than $2 trillion since President Trump took office.
Chart of the Week: The Soaring Cost of Insulin
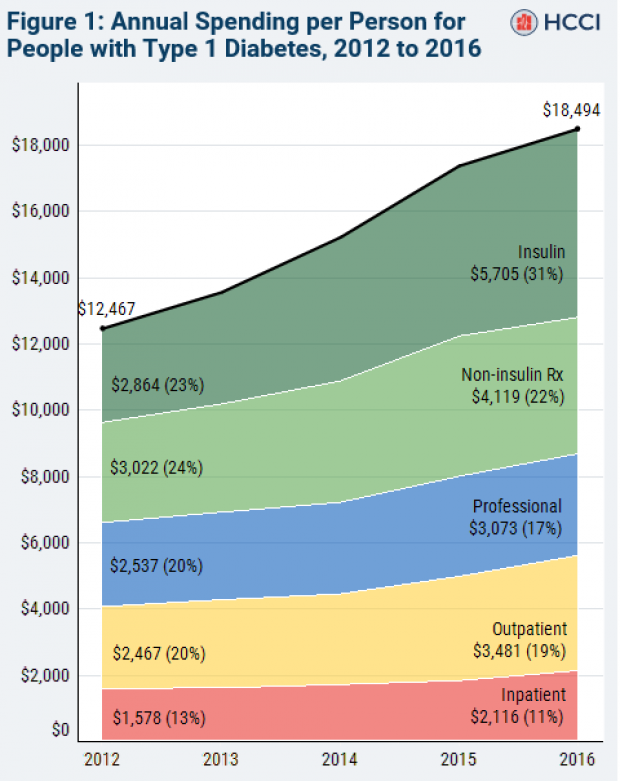
The cost of insulin used to treat Type 1 diabetes nearly doubled between 2012 and 2016, according to an analysis released this week by the Health Care Cost Institute. Researchers found that the average point-of-sale price increased “from $7.80 a day in 2012 to $15 a day in 2016 for someone using an average amount of insulin (60 units per day).” Annual spending per person on insulin rose from $2,864 to $5,705 over the five-year period. And by 2016, insulin costs accounted for nearly a third of all heath care spending for those with Type 1 diabetes (see the chart below), which rose from $12,467 in 2012 to $18,494.
Chart of the Day: Shutdown Hits Like a Hurricane

The partial government shutdown has hit the economy like a hurricane – and not just metaphorically. Analysts at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget said Tuesday that the shutdown has now cost the economy about $26 billion, close to the average cost of $27 billion per hurricane calculated by the Congressional Budget Office for storms striking the U.S. between 2000 and 2015. From an economic point of view, it’s basically “a self-imposed natural disaster,” CRFB said.
Chart of the Week: Lowering Medicare Drug Prices
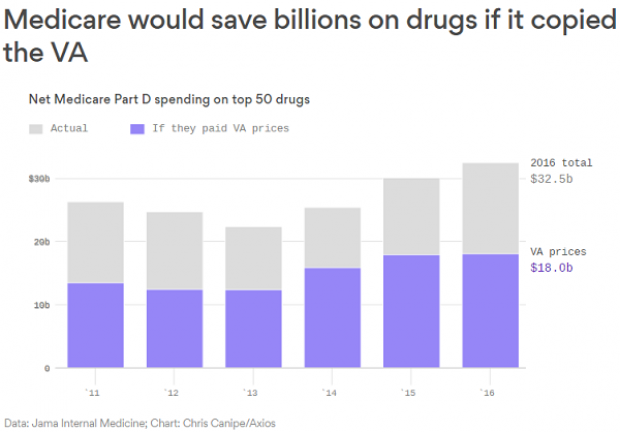
The U.S. could save billions of dollars a year if Medicare were empowered to negotiate drug prices directly with pharmaceutical companies, according to a paper published by JAMA Internal Medicine earlier this week. Researchers compared the prices of the top 50 oral drugs in Medicare Part D to the prices for the same drugs at the Department of Veterans Affairs, which negotiates its own prices and uses a national formulary. They found that Medicare’s total spending was much higher than it would have been with VA pricing.
In 2016, for example, Medicare Part D spent $32.5 billion on the top 50 drugs but would have spent $18 billion if VA prices were in effect – or roughly 45 percent less. And the savings would likely be larger still, Axios’s Bob Herman said, since the study did not consider high-cost injectable drugs such as insulin.