Love Selfies? Now They Can Keep Your Credit Card Safe

MasterCard is appealing to America’s obsession with selfies in an effort to reduce credit card identity theft.
The credit card company is launching a new program that will allow consumers to approve online purchases with a facial scan. At the checkout page, you’ll be asked to take a picture of yourself using your phone instead of entering a password.
Currently, customers can stop hackers from using their credit card on the Web by setting up a “SecureCode,” which requires a password when shopping online. The password system was used in 3 billion transactions last year.
This fall MasterCard will launch a small pilot program involving 500 customers using fingerprints and facial scans. If the test is a success, the company plans on rolling it out publicly afterward. The company is also looking ahead to one day apply voice recognition technology.
To use the new selfie system, customers need to download the MasterCard phone app. Once you pay for something, a pop-up will appear asking for your authorization with either a fingerprint or facial recognition. Using facial recognition, customers stare at the phone, blink once — and bam! All done. The blink is a security measure so thieves can’t just hold up a photo of you. A fingerprint only requires a touch.
Passwords are easily forgotten, stolen or cracked, so the new system is a way to prove your identity using biometrics. Critics of the new system are uncomfortable that the photo or fingerprint a customer puts into his or her phone will transmit to the company’s computer servers. Cybersecurity experts worry the transfer of such information across devices is too big of a privacy risk.
MasterCard wasn’t the first company to develop a facial recognition app — Chinese shopping brand Alibaba demonstrated one in March, but had to postpone the technology’s launch because of security risks found by China’s central bank and police ministry.
Deficit Hits $738.6 Billion in First 8 Months of Fiscal Year

The U.S. budget deficit grew to $738.6 billion in the first eight months of the current fiscal year – an increase of $206 billion, or 38.8%, over the deficit recorded during the same period a year earlier. Bloomberg’s Sarah McGregor notes that the big increase occurred despite a jump in tariff revenues, which have nearly doubled to $44.9 billion so far this fiscal year. But that increase, which contributed to an overall increase in revenues of 2.3%, was not enough to make up for the reduced revenues from the Republican tax cuts and a 9.3% increase in government spending.
Tweet of the Day: Revenues or Spending?

Rep. Kevin Brady (R-TX), ranking member of the House Ways and Means Committee and one of the authors of the 2017 Republican tax overhaul, told The Washington Post’s Heather Long Tuesday that the budget deficit is driven by excess spending, not a shortfall in revenues in the wake of the tax cuts. The Wall Street Journal’s Kate Davidson provided some inconvenient facts for Brady’s claim in a tweet, pointing out that government revenues as a share of GDP have fallen significantly since 2015, while spending has remained more or less constant.
Chart of the Day: The Decline in IRS Audits

Reviewing the recent annual report on tax statistics from the IRS, Robert Weinberger of the Tax Policy Center says it “tells a story of shrinking staff, fewer audits, and less customer service.” The agency had 22% fewer personnel in 2018 than it did in 2010, and its enforcement budget has fallen by nearly $1 billion, Weinberger writes. One obvious effect of the budget cuts has been a sharp reduction in the number of audits the agency has performed annually, which you can see in the chart below.
Number of the Day: $102 Million

President Trump’s golf playing has cost taxpayers $102 million in extra travel and security expenses, according to an analysis by the left-leaning HuffPost news site.
“The $102 million total to date spent on Trump’s presidential golfing represents 255 times the annual presidential salary he volunteered not to take. It is more than three times the cost of special counsel Robert Mueller’s investigation that Trump continually complains about. It would fund for six years the Special Olympics program that Trump’s proposed budget had originally cut to save money,” HuffPost’s S.V. Date writes.
Date says the White House did not respond to HuffPost’s requests for comment.
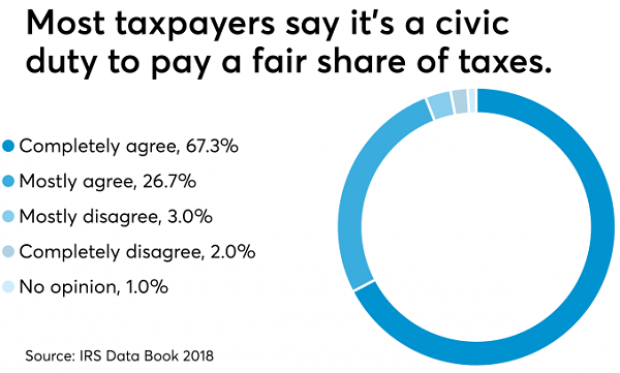
Americans See Tax-Paying as a Duty

The IRS may not be conducting audits like it used to, but according to the agency’s Data Book for 2018, most Americans still believe it’s not acceptable to cheat on your taxes. About 67% of respondents to an IRS opinion survey “completely agree” that it’s a civic duty to pay “a fair share of taxes,” and another 26% “mostly agree,” bringing the total in agreement to over 90%. Accounting Today says that attitude has been pretty consistent over the last decade.