Hillary Too Expensive? Get Chelsea Clinton at a Discount

If you’re turned off by the astronomical speaking fees commanded by the former Secretary of State and her former president husband, you have an option: You can go Clinton shopping.
Hillary and Bill Clinton earned in excess of $25 million for delivering 104 speeches between 2014 and the first three months of 2015, including $11 million that Hillary Clinton collected delivering 51 speeches, according to reports filed with the Federal Election Commission.
Related: Hillary Clinton’s Achilles' Heel: Trust
While Hillary’s fees varied, they typically exceeded a quarter-million-dollars a pop and went as high as $300,000, although she generally donated the funds to the Clinton family’s global foundation.
But at least one sticker-shocked university balked at her price and settled for a bargain basement alternative – daughter Chelsea Clinton.
As The Washington Post recounted on Tuesday, officials of the University of Missouri at Kansas City were in the market for a celebrity speaker to headline a gala luncheon marking the opening of a women’s hall of fame in early 2014. Initially, they thought of inviting Clinton’s 34-year old daughter to deliver brief remarks at the event.
When Chelsea’s speaking agency responded that she probably wouldn’t be available, university officials decided to “shoot for the moon” and invite her mother, the presumptive 2016 Democratic presidential candidate, to appear instead. However, they were stunned when the answer came back that Hillary Clinton indeed would be available but it would cost them $275,000.
Related: College Students Outraged over Hillary Clinton’s Massive Speaking Fees
University officials regrouped and resumed their hunt for a speaker. Then word came back that Chelsea Clinton was available to speak after all – and for the relatively modest fee of $65,000. Likely still reeling from the Hillary demand, university officials jumped at the offer.
Chelsea Clinton appeared at the luncheon on Feb. 24, 2014, and here’s what her schedule called for: a 10-minute speech followed by a 20-minute, moderated question-and-answer session and a half-hour posing for pictures with VIPs off-stage. As with Hillary Clinton’s paid speeches at universities, Chelsea Clinton directed her fee to the Bill, Hillary and Chelsea Clinton Foundation.
School officials said Chelsea’s appearance, which was covered by private donations, was well worth the money. Reactions to the story on social media were less positive, with anti-Clinton commentators having a field day mocking America’s one-time and perhaps future first family.
Tax Refunds Rebound

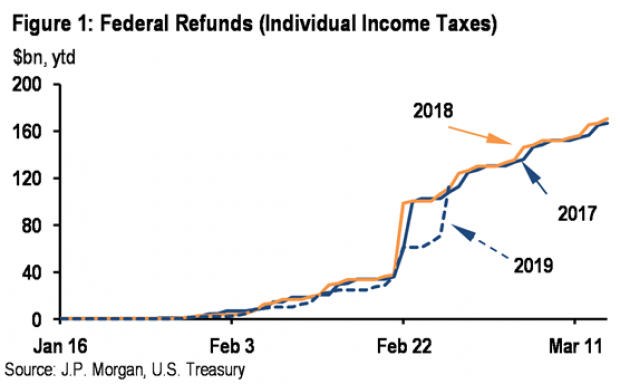
Smaller refunds in the first few weeks of the current tax season were shaping up to be a political problem for Republicans, but new data from the IRS shows that the value of refund checks has snapped back and is now running 1.3 percent higher than last year. The average refund through February 23 last year was $3,103, while the average refund through February 22 of 2019 was $3,143 – a difference of $40. The chart below from J.P. Morgan shows how refunds performed over the last 3 years.
Number of the Day: $22 Trillion

The total national debt surpassed $22 trillion on Monday. Total public debt outstanding reached $22,012,840,891,685.32, to be exact. That figure is up by more than $1.3 trillion over the past 12 months and by more than $2 trillion since President Trump took office.
Chart of the Week: The Soaring Cost of Insulin
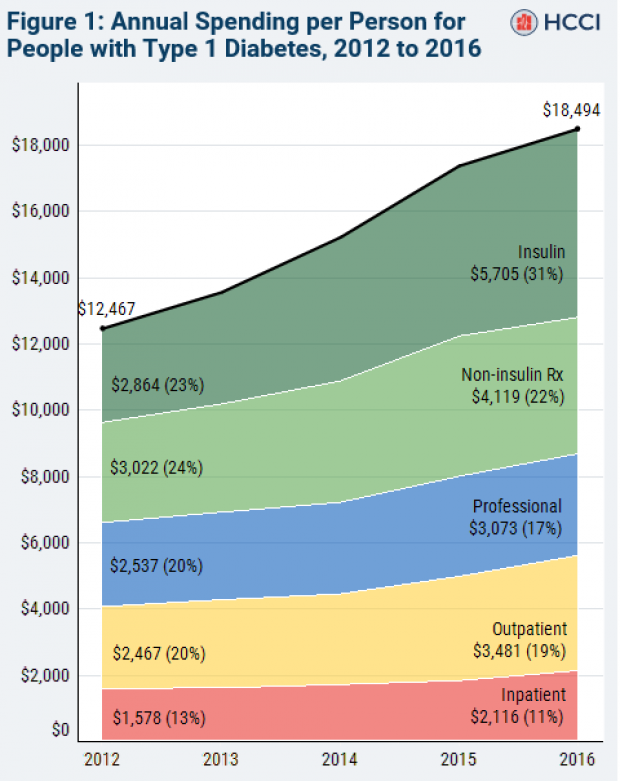
The cost of insulin used to treat Type 1 diabetes nearly doubled between 2012 and 2016, according to an analysis released this week by the Health Care Cost Institute. Researchers found that the average point-of-sale price increased “from $7.80 a day in 2012 to $15 a day in 2016 for someone using an average amount of insulin (60 units per day).” Annual spending per person on insulin rose from $2,864 to $5,705 over the five-year period. And by 2016, insulin costs accounted for nearly a third of all heath care spending for those with Type 1 diabetes (see the chart below), which rose from $12,467 in 2012 to $18,494.
Chart of the Day: Shutdown Hits Like a Hurricane

The partial government shutdown has hit the economy like a hurricane – and not just metaphorically. Analysts at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget said Tuesday that the shutdown has now cost the economy about $26 billion, close to the average cost of $27 billion per hurricane calculated by the Congressional Budget Office for storms striking the U.S. between 2000 and 2015. From an economic point of view, it’s basically “a self-imposed natural disaster,” CRFB said.
Chart of the Week: Lowering Medicare Drug Prices
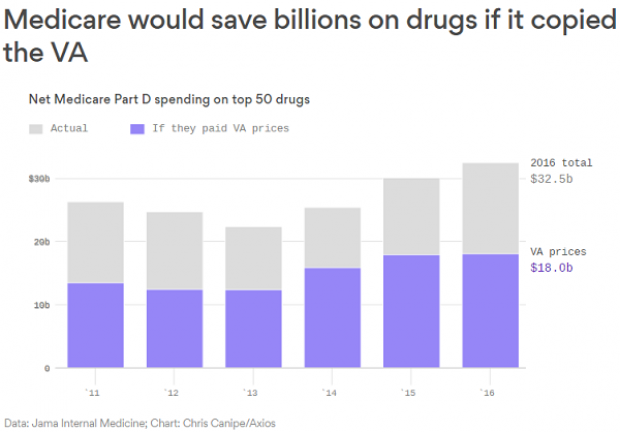
The U.S. could save billions of dollars a year if Medicare were empowered to negotiate drug prices directly with pharmaceutical companies, according to a paper published by JAMA Internal Medicine earlier this week. Researchers compared the prices of the top 50 oral drugs in Medicare Part D to the prices for the same drugs at the Department of Veterans Affairs, which negotiates its own prices and uses a national formulary. They found that Medicare’s total spending was much higher than it would have been with VA pricing.
In 2016, for example, Medicare Part D spent $32.5 billion on the top 50 drugs but would have spent $18 billion if VA prices were in effect – or roughly 45 percent less. And the savings would likely be larger still, Axios’s Bob Herman said, since the study did not consider high-cost injectable drugs such as insulin.