Why U.S. Productivity May Be Worse Than We Think

The new economy may be making it easier for people to work from home and in other non-office settings, but it isn’t necessarily making us more productive.
This week, the Bureau of Labor statistics released new data, which showed that Americans spent more time working last year than at any time in the survey’s 12-year history. However, employers aren’t paying workers for those additional hours worked, according to a new research note from Michael Feroli, Chief Economist at J.P. Morgan
That’s bad news for workers, who are doing additional work without earning any additional compensation, but it’s also bad news for the economy. The BLS measures productivity growth (output divided by hours worked) based on the number of hours reported by the employer.
Related: The Do’s and Don’t’s of Boosting Your Productivity
Even by that measure, productivity expanded just 0.6 percent per year from 2010 to 2014, compared to 2.1 percent per year from 2003 to 2009. But when looking at productivity growth based on hours worked from an employees’ perspective, productivity has remained totally flat since 2010, according to Feroli.
What’s behind the discrepancy? Feroli writes that it may have to do with the way we work in today’s economy. “Technology can tether one to the office every minute of the day and in every place, regardless of whether the employer pays for that degree of connectedness.”
GOP Tax Cuts Getting Less Popular, Poll Finds

Friday marked the six-month anniversary of President Trump’s signing the Republican tax overhaul into law, and public opinion of the law is moving in the wrong direction for the GOP. A Monmouth University survey conducted earlier this month found that 34 percent of the public approves of the tax reform passed by Republicans late last year, while 41 percent disapprove. Approval has fallen by 6 points since late April and disapproval has slipped 3 points. The percentage of people who aren’t sure how they feel about the plan has risen from 16 percent in April to 24 percent this month.
Other findings from the poll of 806 U.S. adults:
- 19 percent approve of the job Congress is doing; 67 percent disapprove
- 40 percent say the country is heading in the right direction, up from 33 percent in April
- Democrats hold a 7-point edge in a generic House ballot
Special Tax Break Zones Defined for All 50 States

The U.S. Treasury has approved the final group of opportunity zones, which offer tax incentives for investments made in low-income areas. The zones were created by the tax law signed in December.
Bill Lucia of Route Fifty has some details: “Treasury says that nearly 35 million people live in the designated zones and that census tracts in the zones have an average poverty rate of about 32 percent based on figures from 2011 to 2015, compared to a rate of 17 percent for the average U.S. census tract.”
Click here to explore the dynamic map of the zones on the U.S. Treasury website.
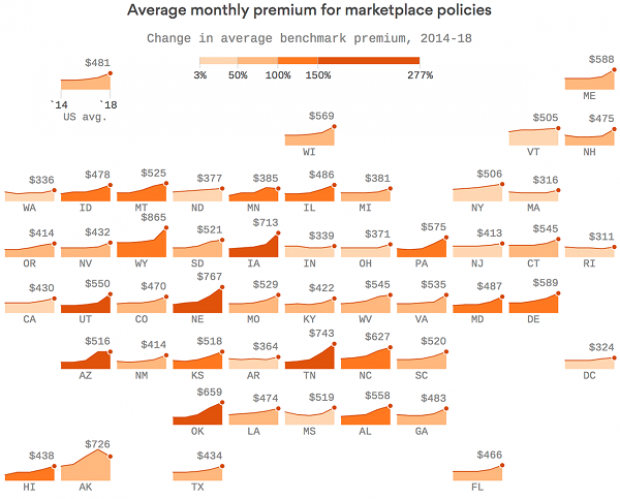
Map of the Day: Affordable Care Act Premiums Since 2014

Axios breaks down how monthly premiums on benchmark Affordable Care Act policies have risen state by state since 2014. The average increase: $481.
Obamacare Repeal Would Lead to 17.1 Million More Uninsured in 2019: Study

A new analysis by the Urban Institute finds that if the Affordable Care Act were eliminated entirely, the number of uninsured would rise by 17.1 million — or 50 percent — in 2019. The study also found that federal spending would be reduced by almost $147 billion next year if the ACA were fully repealed.
Your Tax Dollars at Work

Mick Mulvaney has been running the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau since last November, and by all accounts the South Carolina conservative is none too happy with the agency charged with protecting citizens from fraud in the financial industry. The Hill recently wrote up “five ways Mulvaney is cracking down on his own agency,” and they include dropping cases against payday lenders, dismissing three advisory boards and an effort to rebrand the operation as the Bureau of Consumer Financial Protection — a move critics say is intended to deemphasize the consumer part of the agency’s mission.
Mulvaney recently scored a small victory on the last point, changing the sign in the agency’s building to the new initials. “The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau does not exist,” Mulvaney told Congress in April, and now he’s proven the point, at least when it comes to the sign in his lobby (h/t to Vox and thanks to Alan Zibel of Public Citizen for the photo, via Twitter).