The Hidden Costs of Home Ownership: $6,000 a Year

Most new homeowners are prepared to pay their mortgages, but they may not be ready for other unavoidable costs that can amount to thousands of dollars every year.
The average homeowner shelled out $6,042 last year in homeowners insurance, property taxes, and utilities, according to a new report from Zillow. The average costs varied by location, with Boston homeowners spending the most ($9,413) and homeowners in Phoenix spending the least ($4,513).
“Home buyers too often fixate on the sticker price or monthly mortgage payment on a house, and don’t budget for the other expenses associated with ownership -- which can add up quickly,” Zillow spokeswoman Amy Bohutinsky said in a statement.
Related: How to Decide if You Should Rent or Buy a Home
The maintenance costs included in the report included things like lawn care and carpet cleaning.
The country’s homeownership rate fell to 63.7 percent in the first quarter, the lowest level since 1989. The rate peaked at 69.2 percent in the fourth quarter of 2004, right before the housing bubble burst.
As rents in many cities continue to skyrocket, however, homeownership may be becoming more appealing. However, in addition to hidden homeownership costs, new buyers should also consider the opportunity costs of potential earnings if buyers had invested their down payment. The New York Times has a handy calculator that incorporates these and other factors to help weigh whether it makes more sense to rent or buy.
Nearly two-thirds of consumers say that home ownership is a “dream come true” and an accomplishment to be proud of, according to a survey released last week by Wells Fargo.
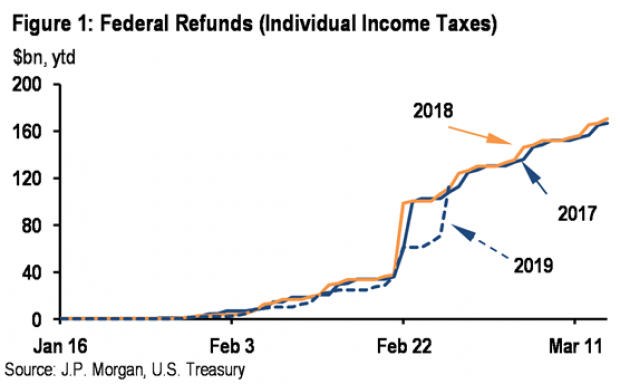
Tax Refunds Rebound

Smaller refunds in the first few weeks of the current tax season were shaping up to be a political problem for Republicans, but new data from the IRS shows that the value of refund checks has snapped back and is now running 1.3 percent higher than last year. The average refund through February 23 last year was $3,103, while the average refund through February 22 of 2019 was $3,143 – a difference of $40. The chart below from J.P. Morgan shows how refunds performed over the last 3 years.
Number of the Day: $22 Trillion

The total national debt surpassed $22 trillion on Monday. Total public debt outstanding reached $22,012,840,891,685.32, to be exact. That figure is up by more than $1.3 trillion over the past 12 months and by more than $2 trillion since President Trump took office.
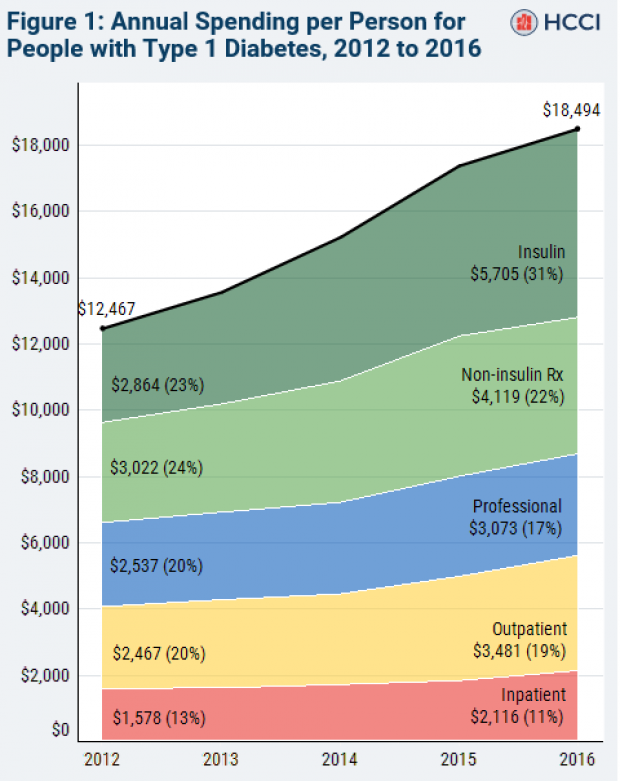
Chart of the Week: The Soaring Cost of Insulin
The cost of insulin used to treat Type 1 diabetes nearly doubled between 2012 and 2016, according to an analysis released this week by the Health Care Cost Institute. Researchers found that the average point-of-sale price increased “from $7.80 a day in 2012 to $15 a day in 2016 for someone using an average amount of insulin (60 units per day).” Annual spending per person on insulin rose from $2,864 to $5,705 over the five-year period. And by 2016, insulin costs accounted for nearly a third of all heath care spending for those with Type 1 diabetes (see the chart below), which rose from $12,467 in 2012 to $18,494.
Chart of the Day: Shutdown Hits Like a Hurricane

The partial government shutdown has hit the economy like a hurricane – and not just metaphorically. Analysts at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget said Tuesday that the shutdown has now cost the economy about $26 billion, close to the average cost of $27 billion per hurricane calculated by the Congressional Budget Office for storms striking the U.S. between 2000 and 2015. From an economic point of view, it’s basically “a self-imposed natural disaster,” CRFB said.
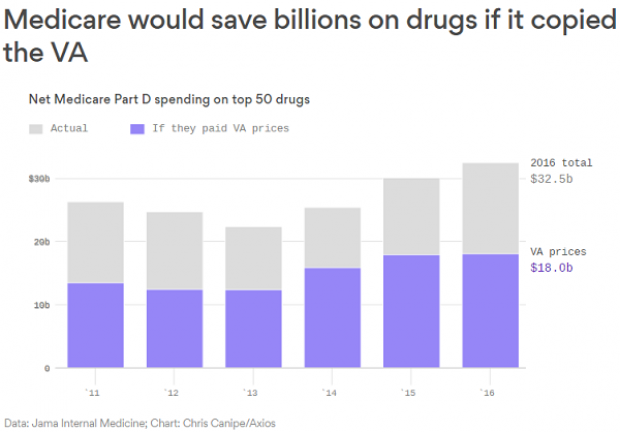
Chart of the Week: Lowering Medicare Drug Prices
The U.S. could save billions of dollars a year if Medicare were empowered to negotiate drug prices directly with pharmaceutical companies, according to a paper published by JAMA Internal Medicine earlier this week. Researchers compared the prices of the top 50 oral drugs in Medicare Part D to the prices for the same drugs at the Department of Veterans Affairs, which negotiates its own prices and uses a national formulary. They found that Medicare’s total spending was much higher than it would have been with VA pricing.
In 2016, for example, Medicare Part D spent $32.5 billion on the top 50 drugs but would have spent $18 billion if VA prices were in effect – or roughly 45 percent less. And the savings would likely be larger still, Axios’s Bob Herman said, since the study did not consider high-cost injectable drugs such as insulin.