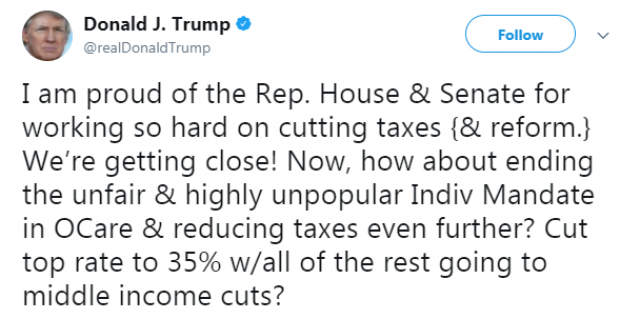The 2016 Presidential Debates Could Become a Slugfest

Few could doubt the impact of nationally televised presidential debates after Republican Mitt Romney set President Obama back on his heels in their first encounter in October 2012.
Romney was articulate and aggressive while Obama appeared frazzled and very much off his game. Romney’s commanding performance helped the former Massachusetts governor briefly energize his floundering campaign and regain its momentum.
Related: Clinton Plays the Gender Card as a Campaign Strategy -
Moreover, with home viewership topping 67 million, the debate -- moderated by Jim Lehrer, the former news anchor for the PBS News Hour – broke a 32-year gross viewership record dating back to the first debate between Democratic President Jimmy Carter and Republican challenger Ronald Reagan in 1980.
Yet amid dramatic changes in political campaign tactics and fundraising and the way Americans consume the news, these televised general election presidential debates actually are suffering from diminished reach.
A new study issued on Wednesday by the Annenberg Public Policy Center at the University of Pennsylvania seemed to compare presidential debates to TV entertainment. Their assessment: the more than two-decade old debate format is to blame for the low viewership among millennials, although baby boomer viewers have increased.
Related: Why Marco Rubio Might Just Beat Hillary Clinton
So what to do? In an era when large audiences pay far more attention to “Game of Thrones,” “House of Cards,” “Master Chef” and “So You Think You Can Dance” than to increasingly lengthy presidential campaign seasons, how can the political parties and the National Presidential Debate Commission jazz up the debates to attract and keep a wider audience?
The Annenberg panel, of course, stops well short of recommending the equivalent of no-holds barred political mudwrestling to heighten audience engagement and sustained interest. The goal, the group says, is to expand and enrich debate content and produce a better informed group of voters.
To that end, the advisory group appears anxious to get rid of the moderator or middle man as much as possible and allow the two candidates to set the agenda and duke it out. They want to get rid of the one or more prominent journalists who set the ground rules and determine the pace and course of the evening’s discussion.
Related: GOP Prunes the 2016 Primary Debates Down to Nine
If, for example, Hillary Clinton were to slam, say, Marco Rubio in a debate, Rubio shouldn’t have to wait patiently for his opportunity to reply but should be allowed to jump in with a rejoinder. Think of it as the resurrection of CNN’s Crossfire.
To add a smidgeon of Jeopardy to the proceedings, each candidate would have a total of 45 minutes to spend to make their case or defend it.
While the candidates would have plenty of opportunity to get their political messages across, they would also have to respond quickly to attacks. A well-scripted candidate wouldn’t necessarily do well in that setting, and the possibility of “oops” moments would be increased. Welcome to reality TV, Beltway style.
Related: The GOP Hunger Games: Who Will Make the Debate Cut?
Ah….but dead air is not an option, so a filibuster is off the table. No answer, rebuttal or question could exceed three minutes, according to the panel. When a candidate runs out of total time, he or she has exhausted the right to speak. Remaining time at the end of the moderator-posed topics can be used for a closing statement.
The recommendations are advisory only and it will be up to the presidential debate commission and the national parties to iron out the final ground rules next year.
Trump: Repeal the Obamacare Mandate to Cut the Top Tax Rate

President Trump repeated his call Monday to repeal the Affordable Care Act’s individual mandate as part of the tax bill. In a tweet — geotagged from Pennsylvania, not the Philippines , where Trump currently is — Trump added that the billions in savings from ending the mandate should be used to cut the top marginal rate to 35 percent and the rest on cuts for the middle class.
The Congressional Budget Office said last week that eliminating the mandate would save $338 billion over the next decade.
The current version of the House tax bill keeps the top individual income tax rate at 39.6 percent, while the Senate bill lowers it to 38.5 percent. However, mandate repeal is not currently part of either tax bill, and, as The New York Times notes, “repeal of the individual mandate was not on the list of 355 amendments that the [Senate Finance Committee] released on Sunday night.”
Tax Reform Is Hard, but the GOP Could Have Made This Easier
The Tax Policy Center’s William G. Gale writes that the GOP’s approach to the tax bill combines a $5.8 trillion tax cut with a $4.3 trillion tax increase to offset the costs. There may have been an easier way. “What if the House GOP simply tried to cut business and individual taxes by $1.5 trillion. No offsets needed. They could have distributed small tax cuts to middle-income individuals by, say, modestly expanding the earned income tax credit and raising the standard deduction. And they could have trimmed the top corporate tax rate by a few percentage points. It would not have been base-broadening tax reform, but neither is the current bill. ... Tax reform is never easy, but crafting the bill this way has vastly increased the challenge of passing it.”
Alan Greenspan: Deal with the National Debt Before Cutting Taxes

Former Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan is warning that sharply cutting taxes right now would be an economic “mistake.”
In an interview with Maria Bartiromo on the Fox Business Network Thursday, the 91-year-old Greenspan said it’s more important for President Trump and Congress to put the nation on a sustainable fiscal path by addressing rising entitlement spending driven by the aging of the U.S. population.
“Frankly, I think what we ought to be concerned about is the fact the federal debt is rising at a very rapid pace, and there’s nothing in this bill that will essentially stop that from happening," Greenspan said. "So my view is that we’re premature on fiscal stimulus, whether it’s tax cuts or expenditure increases. We’ve got to get the debt stabilized before we can even think in those terms.”
GOP’s Estate-Tax Repeal Details Would Save Super-Rich Tens of Billions Extra

It’s no surprise that the House Republicans’ tax bill includes the eventual repeal of the estate tax, a long-held GOP goal. But The Washington Post’s Glenn Kessler highlights an unexpectedly generous aspect of the current bill: It “allows the beneficiaries of estates to not pay capital gains taxes on the increase in value of assets held by the estates. That has not been a feature of most previous estate-tax bills.”
Currently, estates face a federal tax if they’re valued at more than $5.49 million for individuals or almost $11 million for couples. But, for tax purposes, the value of assets passed on to heirs gets “stepped-up” or reset to their value at the time of death. Kessler’s example: “Imagine a home that had been purchased for $250,000 but was now worth $1 million. The ‘stepped-up basis’ would be $1 million. If the heirs sold the house for $1.1 million, they would only owe capital-gains tax on the $100,000 difference, not the $850,000 difference from the original purchase price.”
The GOP bill repeals the estate tax, but also keeps the stepped-up basis — a seemingly small detail that creates a huge tax shelter. It means that heirs of large estates would save tens of billions of dollars a year when they sell assets that have appreciated in value over time — or, as Kessler puts it, that the bill will allow “tens of billions of untapped capital gains to remain beyond the reach of the U.S. government.”
Republicans Are Still Coming After Obamacare’s Individual Mandate

Speaker Paul Ryan said Sunday that House Republicans are still considering a repeal of the Obamacare individual mandate as part of their tax bill. "We have an active conversation with our members and a whole host of ideas on things to add to this bill. And that’s one of the things that’s being discussed," Ryan said on Fox News. President Trump touted the idea in a tweet last week, and Sens. Tom Cotton and Rand Paul have recently spoken in favor of using the tax bill to eliminate the mandate. The move would save the government $416 billion over 10 years as roughly 15 million people go without insurance due to lower spending on subsidies and health care services, according to the CBO. Those savings could be appealing as Republicans look for revenues in their revised tax bill. But if the controversial repeal of the mandate isn’t included in the tax bill, the White House is reportedly ready to roll out an executive order weakening the requirement that taxpayers provide proof of insurance to avoid paying a penalty.