Home Buying Gets Easier as Down Payments Dip

One hurdle to first-time homebuyers is starting to get a little lower: The average down payment for a home fell to less than 15 percent in the first quarter of 2015 to its lowest level since early 2012. The average down payment for the quarter was $57,710, according to RealtyTrac.
The lower down payments reflect new loan programs recently introduced by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, and lower insurance premiums for Federal Housing Authority Loans. The market is also adjusting as large, institutional investors who had been buying starter homes as rental investments dial back.
Related: U.S. Homeownership Dips, But Household Formation Rises
“Down payment trends in the first quarter indicate that first-time homebuyers are finally starting to come out of the woodwork, albeit gradually,” RealtyTrac vice president Daren Blomquist said in a statement.
Broken down by type of loan, the average down payment for conventional loans was 18.4 percent ($72,590), and the average down payment for FHA loans was just 2.9 percent ($7,609). FHA loans as a share of all mortgages increased from 21 percent in January to 25 percent in March.
Among the country’s largest counties, Wayne County in Detroit, Mich., had the lowest average down payment (12 percent), and New York had the highest (37 percent).
While lower down payments are good news for first-time homebuyers, they also are a reminder of practices that led to the housing bubble that began to burst in late 2006 and contributed to the financial crisis. During the height of the boom, buyers were able to purchase homes that they couldn’t really afford by putting little or no money down on the property.
Tweet of the Day: The Black Hole of Big Pharma
Billionaire John D. Arnold, a former energy trader and hedge fund manager turned philanthropist with a focus on health care, says Big Pharma appears to have a powerful hold on members of Congress.
Arnold pointed out that PhRMA, the main pharmaceutical industry lobbying group, had revenues of $459 million in 2018, and that total lobbying on behalf of the sector probably came to about $1 billion last year. “I guess $1 bil each year is an intractable force in our political system,” he concluded.
Warren’s Taxes Could Add Up to More Than 100%

The Wall Street Journal’s Richard Rubin says Elizabeth Warren’s proposed taxes could claim more than 100% of income for some wealthy investors. Here’s an example Rubin discussed Friday:
“Consider a billionaire with a $1,000 investment who earns a 6% return, or $60, received as a capital gain, dividend or interest. If all of Ms. Warren’s taxes are implemented, he could owe 58.2% of that, or $35 in federal tax. Plus, his entire investment would incur a 6% wealth tax, i.e., at least $60. The result: taxes as high as $95 on income of $60 for a combined tax rate of 158%.”
In Rubin’s back-of-the-envelope analysis, an investor worth $2 billion would need to achieve a return of more than 10% in order to see any net gain after taxes. Rubin notes that actual tax bills would likely vary considerably depending on things like location, rates of return, and as-yet-undefined policy details. But tax rates exceeding 100% would not be unusual, especially for billionaires.
Biden Proposes $1.3 Trillion Infrastructure Plan

Joe Biden on Thursday put out a $1.3 trillion infrastructure proposal. The 10-year “Plan to Invest in Middle Class Competitiveness” calls for investments to revitalize the nation’s roads, highways and bridges, speed the adoption of electric vehicles, launch a “second great railroad revolution” and make U.S. airports the best in the world.
“The infrastructure plan Joe Biden released Thursday morning is heavy on high-speed rail, transit, biking and other items that Barack Obama championed during his presidency — along with a complete lack of specifics on how he plans to pay for it all,” Politico’s Tanya Snyder wrote. Biden’s campaign site says that every cent of the $1.3 trillion would be paid for by reversing the 2017 corporate tax cuts, closing tax loopholes, cracking down on tax evasion and ending fossil-fuel subsidies.
Read more about Biden’s plan at Politico.
Number of the Day: 18 Million

There were 18 million military veterans in the United States in 2018, according to the Census Bureau. That figure includes 485,000 World War II vets, 1.3 million who served in the Korean War, 6.4 million from the Vietnam War era, 3.8 million from the first Gulf War and another 3.8 million since 9/11. We join with the rest of the country today in thanking them for their service.
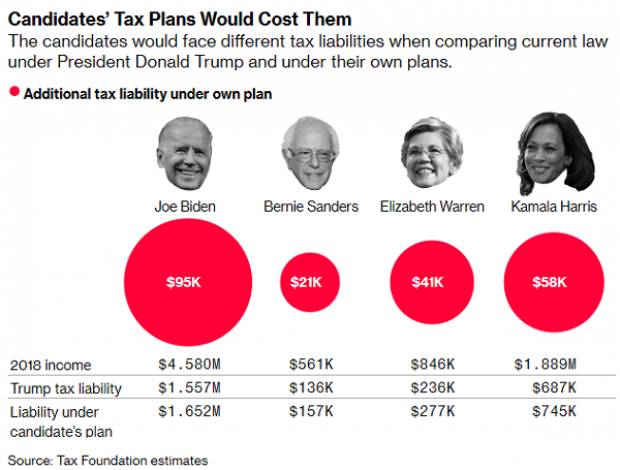
Chart of the Day: Dem Candidates Face Their Own Tax Plans

Democratic presidential candidates are proposing a variety of new taxes to pay for their preferred social programs. Bloomberg’s Laura Davison and Misyrlena Egkolfopoulou took a look at how the top four candidates would fare under their own tax proposals.