Former CBO Chief: Congress Never Meant to Limit Obamacare Subsidies

A Supreme Court ruling expected this summer will determine whether the federal government can subsidize the insurance costs of individuals in states that did not establish their own health care exchanges under the Affordable Care Act.
Douglas Elmendorf was the director of the Congressional Budget Office when Congress debated the bill, and on Tuesday he provided some ammunition to backers of the law who insist that that Congress did not intend to prevent payments of subsidies to consumers in states using the federal exchange.
Related: How Obamacare Could Be Squeezing Consumer Spending
In an interview with CNBC’s John Harwood at the Peter G. Peterson Foundation’s 2015 Fiscal Summit*, Elmendorf said that before the ACA passed, the CBO analyzed the bill for members of Congress, many of whom were powerfully opposed to it. At the time, he said, there was a common understanding on Capitol Hill that the subsidies would be available to states regardless of the status of their exchanges.
“That analysis was subject to a lot of very intense scrutiny and a lot of questions,” he said. “My colleagues and I can remember no occasion on which anybody asked why we were expecting subsidies to be paid in all states regardless of whether they established exchanges or not. And if people had not had this common understanding…then I’m sure we would have had a lot of questions about that.”
Pressed by Harwood, Elmendorf added, “My colleagues and I talked to a lot of people, with a lot of questions about nearly every aspect of the analysis that we did…and we could not remember anybody asking us any questions about what would happen in the federal exchange different from what would happen in the state exchanges.”
Even so, the language of the law states that the subsidies would apply to exchanges “established by the State” and the Supreme Court will decide how literally those words must be interpreted.
*Pete Peterson also funds The Fiscal Times.
Deficit Hits $738.6 Billion in First 8 Months of Fiscal Year

The U.S. budget deficit grew to $738.6 billion in the first eight months of the current fiscal year – an increase of $206 billion, or 38.8%, over the deficit recorded during the same period a year earlier. Bloomberg’s Sarah McGregor notes that the big increase occurred despite a jump in tariff revenues, which have nearly doubled to $44.9 billion so far this fiscal year. But that increase, which contributed to an overall increase in revenues of 2.3%, was not enough to make up for the reduced revenues from the Republican tax cuts and a 9.3% increase in government spending.
Tweet of the Day: Revenues or Spending?

Rep. Kevin Brady (R-TX), ranking member of the House Ways and Means Committee and one of the authors of the 2017 Republican tax overhaul, told The Washington Post’s Heather Long Tuesday that the budget deficit is driven by excess spending, not a shortfall in revenues in the wake of the tax cuts. The Wall Street Journal’s Kate Davidson provided some inconvenient facts for Brady’s claim in a tweet, pointing out that government revenues as a share of GDP have fallen significantly since 2015, while spending has remained more or less constant.
Chart of the Day: The Decline in IRS Audits

Reviewing the recent annual report on tax statistics from the IRS, Robert Weinberger of the Tax Policy Center says it “tells a story of shrinking staff, fewer audits, and less customer service.” The agency had 22% fewer personnel in 2018 than it did in 2010, and its enforcement budget has fallen by nearly $1 billion, Weinberger writes. One obvious effect of the budget cuts has been a sharp reduction in the number of audits the agency has performed annually, which you can see in the chart below.
Number of the Day: $102 Million

President Trump’s golf playing has cost taxpayers $102 million in extra travel and security expenses, according to an analysis by the left-leaning HuffPost news site.
“The $102 million total to date spent on Trump’s presidential golfing represents 255 times the annual presidential salary he volunteered not to take. It is more than three times the cost of special counsel Robert Mueller’s investigation that Trump continually complains about. It would fund for six years the Special Olympics program that Trump’s proposed budget had originally cut to save money,” HuffPost’s S.V. Date writes.
Date says the White House did not respond to HuffPost’s requests for comment.
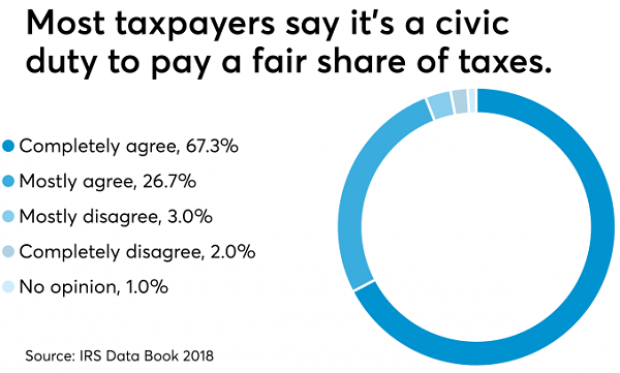
Americans See Tax-Paying as a Duty

The IRS may not be conducting audits like it used to, but according to the agency’s Data Book for 2018, most Americans still believe it’s not acceptable to cheat on your taxes. About 67% of respondents to an IRS opinion survey “completely agree” that it’s a civic duty to pay “a fair share of taxes,” and another 26% “mostly agree,” bringing the total in agreement to over 90%. Accounting Today says that attitude has been pretty consistent over the last decade.