Work-Life Balance: Why Millennials Get Hit Hardest

Even with (or maybe because of) the proliferation of apps and technology to help workers connect with their jobs round-the-clock, finding a balance between work and life is getting harder, according to a new report from Ernst & Young.
The study finds that about half of managers worldwide work more than 40 hours a week, and 40 percent say their hours have increased over the past five years. In addition to technology shifts, the “always on” work culture reflects lingering effects of the recession that has left fewer employees handling larger workloads.
The balancing act is particularly difficult for millennials, who are becoming managers just as they enter into parenthood. U.S. millennial parents are the most likely to have a spouse that’s also working at least full-time, and they’re the less likely than older generations to have taken a career break when having children.
Related: 10 Easy Ways to Improve Your Work-Life Balance
More than one in four millennials is working more after having children, compared to 13 percent of Gen Xers and 16 percent of boomers. Millennial parents place a high value on flexibility, and say that a flexible schedule would make them more engaged, less likely to quit, and more likely to work flexible hours. Even so, one in six says they have suffered a negative consequence for working a flexible schedule.
More than half of those surveyed said that they would make job and career changes in order to find a better work-life balance. Those findings echo the results of a CareerBuilder survey released last year which found that a third of workers don’t want a leadership role because they don’t want to sacrifice work-life balance.
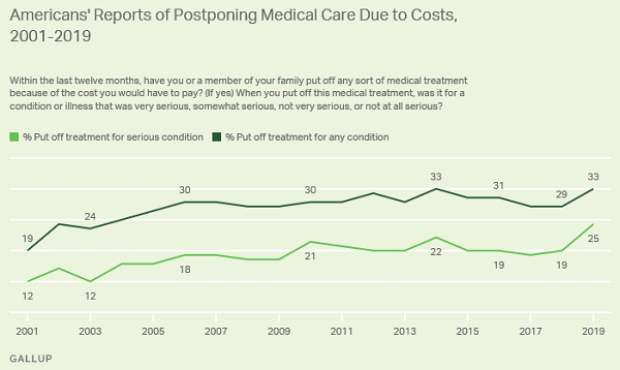
Increasing Number of Americans Delay Medical Care Due to Cost: Gallup

From Gallup: “A record 25% of Americans say they or a family member put off treatment for a serious medical condition in the past year because of the cost, up from 19% a year ago and the highest in Gallup's trend. Another 8% said they or a family member put off treatment for a less serious condition, bringing the total percentage of households delaying care due to costs to 33%, tying the high from 2014.”
Number of the Day: $213 Million

That’s how much the private debt collection program at the IRS collected in the 2019 fiscal year. In the black for the second year in a row, the program cleared nearly $148 million after commissions and administrative costs.
The controversial program, which empowers private firms to go after delinquent taxpayers, began in 2004 and ran for five years before the IRS ended it following a review. It was restarted in 2015 and ran at a loss for the next two years.
Senate Finance Chairman Chuck Grassley (R-IA), who played a central role in establishing the program, said Monday that the net proceeds are currently being used to hire 200 special compliance personnel at the IRS.
US Deficit Up 12% to $342 Billion for First Two Months of Fiscal 2020: CBO

The federal budget deficit for October and November was $342 billion, up $36 billion or 12% from the same period last year, the Congressional Budget Office estimated on Monday. Revenues were up 3% while outlays rose by 6%, CBO said.
Hospitals Sue to Protect Secret Prices

As expected, groups representing hospitals sued the Trump administration Wednesday to stop a new regulation would require them to make public the prices for services they negotiate with insurers. Claiming the rule “is unlawful, several times over,” the industry groups, which include the American Hospital Association, say the rule violates their First Amendment rights, among other issues.
"The burden of compliance with the rule is enormous, and way out of line with any projected benefits associated with the rule," the suit says. In response, a spokesperson for the Department of Health and Human Services said that hospitals “should be ashamed that they aren’t willing to provide American patients the cost of a service before they purchase it.”
See the lawsuit here, or read more at The New York Times.
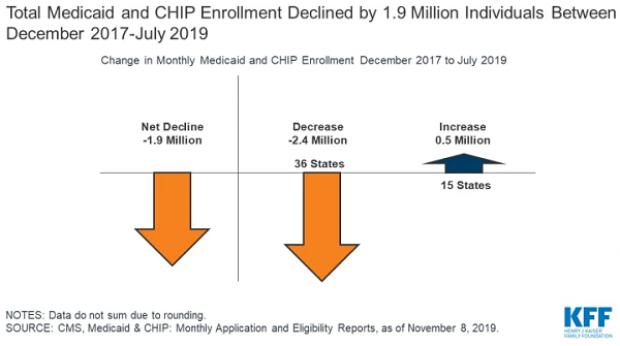
A Decline in Medicaid and CHIP Enrollment
Between December 2017 and July 2019, enrollment in Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) fell by 1.9 million, or 2.6%. The Kaiser Family Foundation provided an analysis of that drop Monday, saying that while some of it was likely caused by enrollees finding jobs that offer private insurance, a significant portion is related to enrollees losing health insurance of any kind. “Experiences in some states suggest that some eligible people may be losing coverage due to barriers maintaining coverage associated with renewal processes and periodic eligibility checks,” Kaiser said.